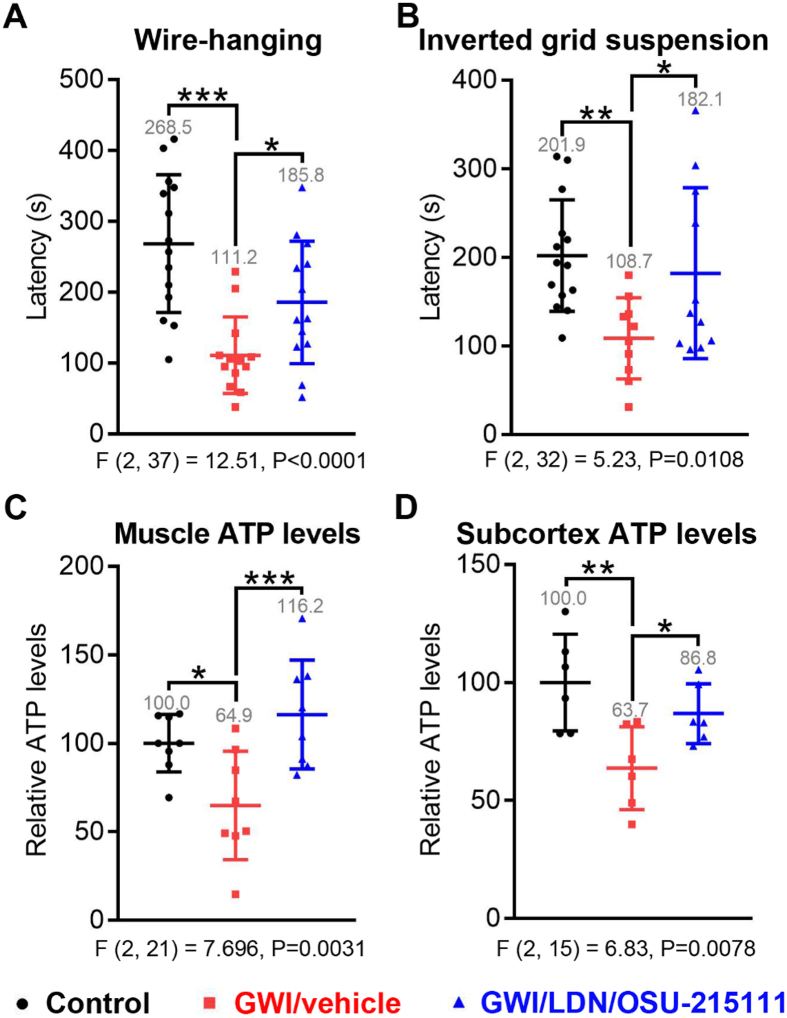
Fig. 6.
GW-exposure causes fatigue and decreased total ATP levels, which can be improved by LDN/OSU-215111. Upon completion of the behavioral assessments in Fig. 5, a subset of mice were assessed for neuromuscular strength by wire-hanging (A) and inverted grid suspension (B) tests. n = 5–8 males and n = 6–7 females each group. GWI/vehicle mice exhibited reduced muscular strength, which was improved by LDN/OSU-215111 treatment (A and B). After the tests, mice were euthanized to measure total ATP levels in limb skeletal muscles (C, n = 8) and subcortex (D, n = 6). GWI/vehicle mice exhibited decreased total ATP levels in both tissues, which were normalized by LDN/OSU-215111 treatment (C and D). Data are presented as mean ± SD. Statistics are based on a one-way ANOVA followed by uncorrected Fisher's LSD method for pairwise comparisons. F and P values for one-way ANOVA are shown. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.