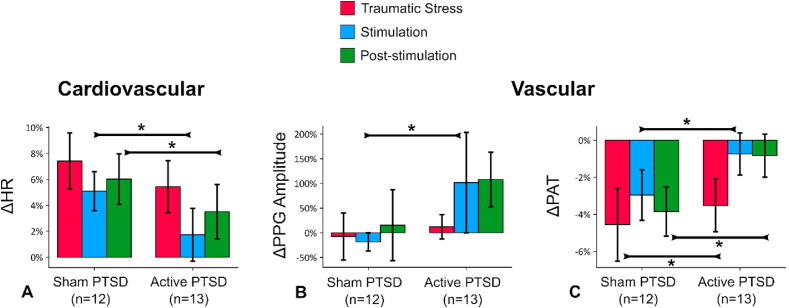
Fig. 2.
tcVNS after traumatic stress: Outcomes for stimulation following traumatic stress (all six scripts). Bars represent the unadjusted mean changes from baseline, error bars: 95% confidence interval (CI), values calculated from raw data, * indicates p < 0.05. β coefficients, adjusted CI, effect sizes (d), and p-values were reported in β (±CI, d, p) format. Active tcVNS group experienced the following relative to sham after traumatic stress after adjustments: (A) Heart rate (HR) decreased during stimulation by 5.6% (±3.6%, d = 0.43, p = 0.003), and following stimulation by 3.9% (±3.0%, d = 0.29, p = 0.013). (B) Photoplethysmogram (PPG) amplitude increased during stimulation by 30.8% (±28.0%, d = 0.41, p = 0.032). (C) Pulse arrival time (PAT) decreased less during traumatic stress by 9.2% (±3.0%, d = 0.15, p < 0.0001), stimulation by 2.2% (±2.2%, d = 0.42, p = 0.045), and following stimulation by 6.2% (±1.9%, d = 0.57, p < 0.0001).