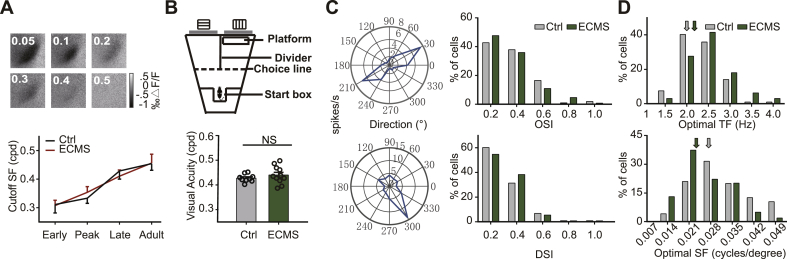
Fig. 2.
ECMS has no effect on the maturation of visual acuity and orientation/direction selectivity.
A. The left column shows the response intensity to different SFs in one control mouse at Late-CP. The right column shows the maturation of the cutoff SF of mouse during the development (Early-CP (Early): Ctrl, 0.31 ± 0.03 cpd, n = 8 mice; ECMS, 0.31 ± 0.02 cpd,n = 8 mice; Peak-CP (Peak): Ctrl, 0.33 ± 0.02 cpd, n = 8 mice; ECMS, 0.35 ± 0.02 cpd,n = 9 mice; Late-CP (Late): Ctrl, 0.43 ± 0.03 cpd, n = 10 mice; ECMS, 0.41 ± 0.02 cpd, n = 9 mice; Adult: Ctrl, 0.45 ± 0.02 cpd,n = 12 mice; ECMS,0.46 ± 0.03 cpd,n = 9 mice. P > 0.05, t-test). B. Schematic of the visual water task is shown in the left column, and the visual acuity of each mouse is shown in the right column (Ctrl, n = 9 mice; ECMS, n = 11 mice, P = 0.35). C. The left column illustrates a cell with high orientation-selectivity and a cell with high direction-selectivity. The right column shows the distribution of OSI (top) and DSI (bottom) in all cells of the control (Ctrl, 103 cells, n = 5 mice) and ECMS groups (128 cells, n = 6 mice). D. The distribution of the optimal TF (top) and SF (bottom) for all cells in the control (Ctrl, 95 cells, n = 5 mice) and ECMS mice (100 cells, n = 6 mice). The arrows indicate the median value of each group. B-D. Grey column represents Ctrl mouse, green column represents ECMS mouse. Error bars, data represents mean ± SEM. A-B. P > 0.05, Student's t-test. C-D. Kolmogorov-Smirnov test.