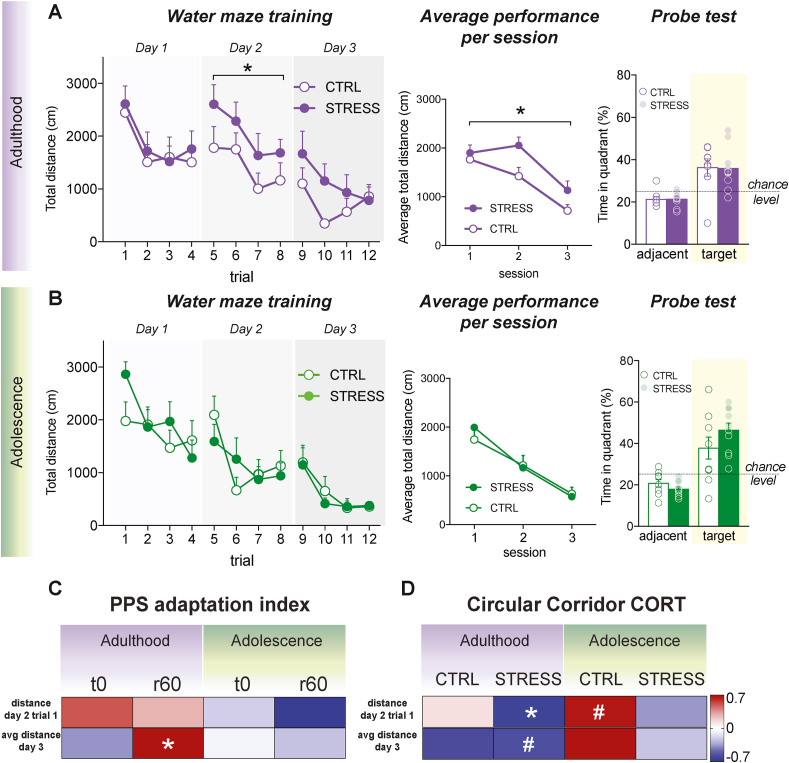
Fig. 4.
Water maze training and probe trial for adult and adolescent rats, as well as correlations of water maze parameters with CORT. A. Left: Adult STRESS rats traveled more distance before finding the platform on the second day of training, compared to CTRL rats. Middle: Compared to CTRL, STRESS rats tested during adulthood showed increased distance in the water maze when the average performance per session was considered. Right: Both CTRL and STRESS adolescent groups exhibited intact memory of the position of the platform during the probe trial, when the platform was absent. No differences were found between the groups. B. Left: No differences were observed between adolescent CTRL and STRESS rats during training in the water maze. Middle: No differences between the groups were observed for the average performance per session. Right: Both CTRL and STRESS adolescent groups exhibited intact memory of the position of the platform during the probe trial, when the platform was absent. No differences were found between the groups. C. Correlation matrix showing correlation coefficients between peak (t0) and recovery (r60) adaptation indexes to peripubertal stress and performance in a in the first long term memory test (trial 1 of the second day of testing) and in the last day of training. Those animals that adapted the less to peripubertal stress (r60) were the more affected while adults and performed the worse in the Morris water maze. D. Correlation matrix between circular corridor CORT response and performance in the water maze, indicating that only in STRESS animals, a more blunted CORT response to the novel environment (lower CORT levels) correlated with impairments in the Morris water maze. Results are expressed as the mean ± S.E.M. Correlation coefficients (r values) in correlation matrix are color-coded. *p < 0.05, #p < 0.10