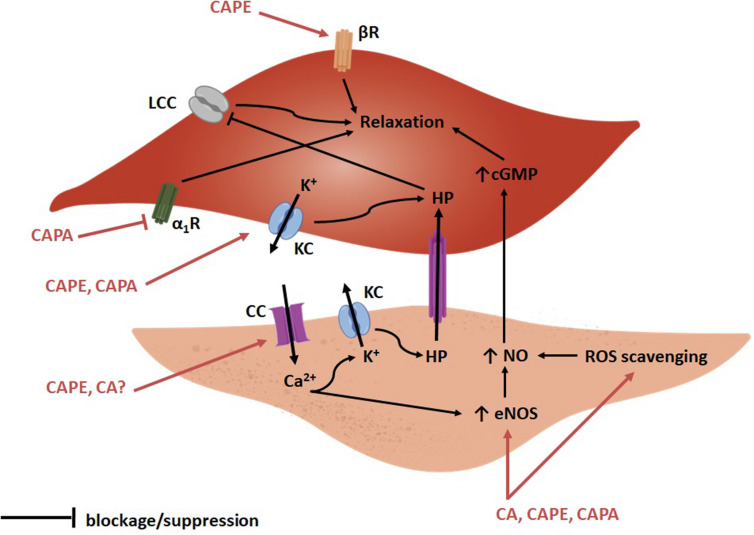
FIGURE 2.
Scheme of the proposed vasorelaxant actions of CA, CAPE and CAPA according to current research. On VSM cells (top) CAPE and CAPA may act on potassium channels (KC), which would lead to potassium efflux and hyperpolarization (HP). Hyperpolarization would contribute to inactivate L-type calcium channels (LCC) and to prevent VSM cell contraction. Additionally, CAPE may activate the beta adrenergic receptor (βR) and contribute to VSM cell relaxation. Additionally, CAPA may exert a weak alpha-1 receptor (α1R) blocking effect. On endothelial cells (bottom), CA and CAPE may act on calcium channels (CC) and lead to calcium influx which, in turn, would open potassium channels (KC) and lead to HP. Hyperpolarization could be communicated to VSM cells via gap junctions and reinforce its relaxation. Calcium may also increase endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) activity and increase NO synthesis, which would diffuse into and relax VSM cells. In addition, CA, CAPE, and CAPA may also scavenge reactive oxygen species (ROS) and prevent NO removal therefore increasing its cellular content.