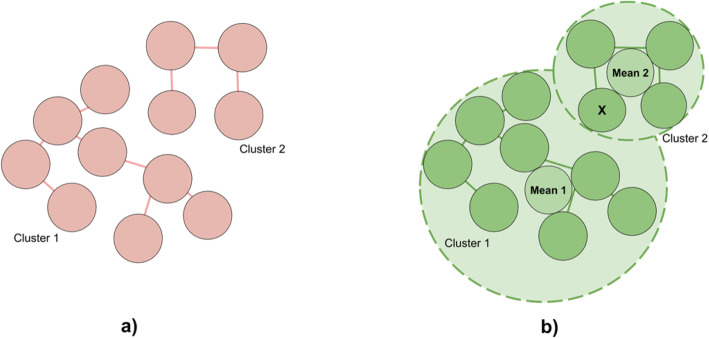
Fig. 5.
Example of overlap-based cluster merging. a Output of threshold-based hierarchical clustering, where circles represent hosts (k-mer distributions), that are connected with an edge if distance (EMD) between them doesn’t exceed a threshold (so that no unrelated hosts are connected). There are 2 clusters that belong to the same outbreak, which means that some related hosts are treated as unrelated. b For each cluster, circles were build, so that mean hosts reside in the center of the circle, and radius is defined as the distance between mean host and furthest host in an outbreak. Circle of cluster 1 intersects with cluster 2 since host X is closer to Mean 1 than furthest host in cluster 1. Therefore, clusters 1 and 2 are merged