Figure 6: Mural cell marker levels are associated with cortical TDP-43 pathology in human volunteers.
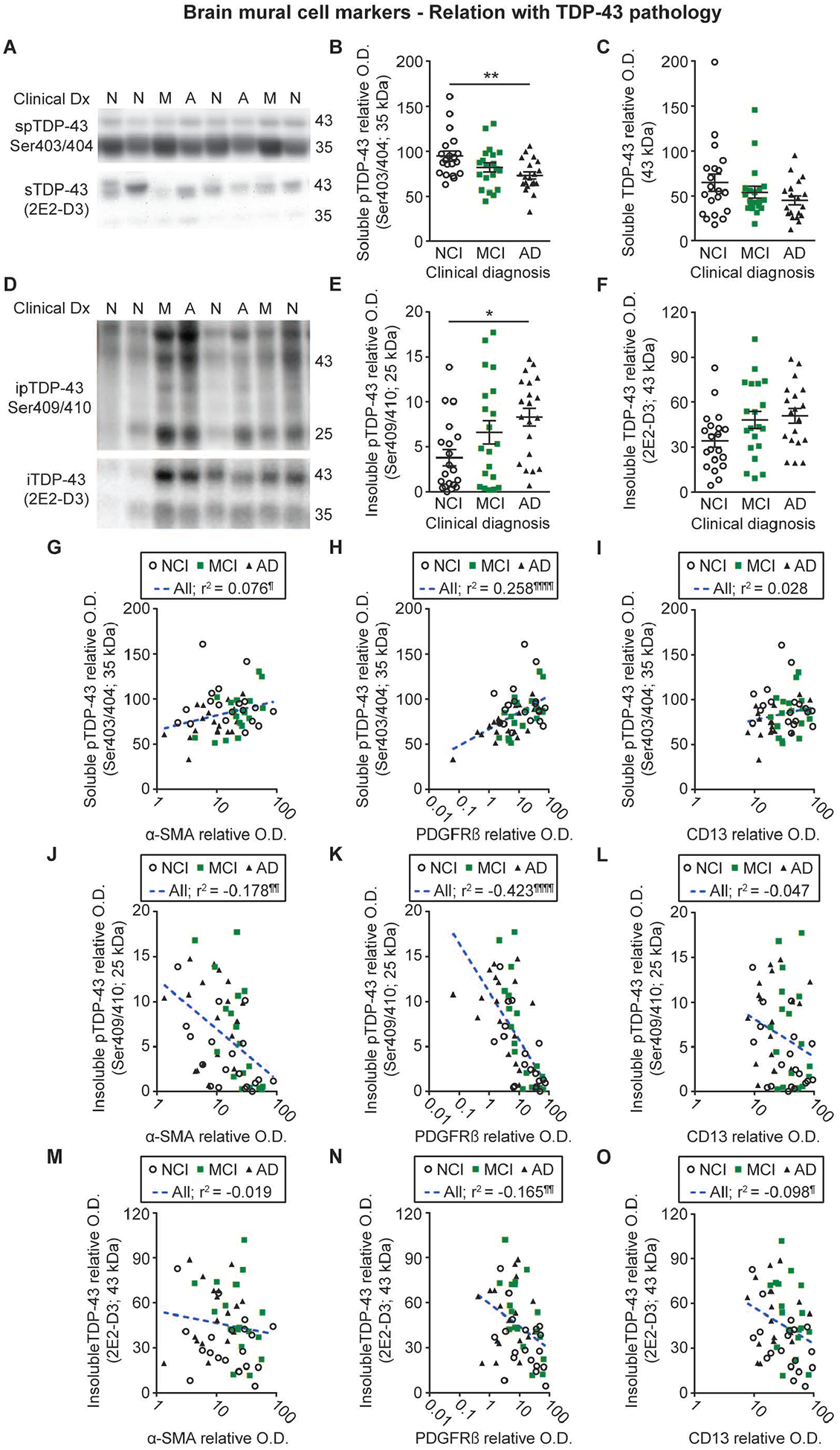
Levels of soluble and insoluble phosphorylated as well as total insoluble TDP-43 were determined by Western immunoblotting in TBS-soluble and formic acid-soluble protein homogenates from the parietal cortex of the same series of donors. Representative photo examples illustrate consecutive bands. Uncropped gels of all immunoblot assays are shown in Figure S4. A-C) Soluble phosphorylated TDP-43 levels were reduced in volunteers clinically classified as AD whereas total soluble TDP-43 levels remained similar between groups. D-F) Insoluble phosphorylated TDP-43 levels were increased in participants with clinical AD while a strong upward trend was noted for total insoluble TDP-43 in the same group. Values in the MCI group were intermediate as compared to the AD and NCI groups. Statistical analysis: one-way analysis of variance followed by a Tukey’s post hoc test, * p < 0.05; ** p 0.01. G-O) Vascular α-SMA and PDGFRβ levels were respectively positively and negatively associated with TBS- and formic acid-soluble phosphorylated TDP-43, while only non-significant trends were observed for CD13. Vascular levels of PDGFRβ and CD13, but not α-SMA, were also negatively associated with total insoluble TDP-43. Statistical analysis: Coefficients of determination (r2) adjusted for age at death and computed after log transformation of relative optical density values for mural cell markers, ¶ p < 0.05; ¶¶ p < 0.01; ¶¶¶ p < 0.001; ¶¶¶¶ p < 0.0001. Abbreviations: α-SMA, smooth muscle alpha actin; A-AD, Alzheimer’s Disease; CD13, aminopeptidase N; Clinical Dx, clinical diagnosis; ipTDP43, insoluble phosphorylated TDP-43; iTDP43, insoluble TDP-43; M-MCI, mild cognitive impairment; N-NCI, healthy controls with no cognitive impairment; O.D., optical density; PDGFRβ, platelet-derived growth factor receptor β; spTDP43, TBS-soluble phosphorylated TDP-43.
