Figure 4.
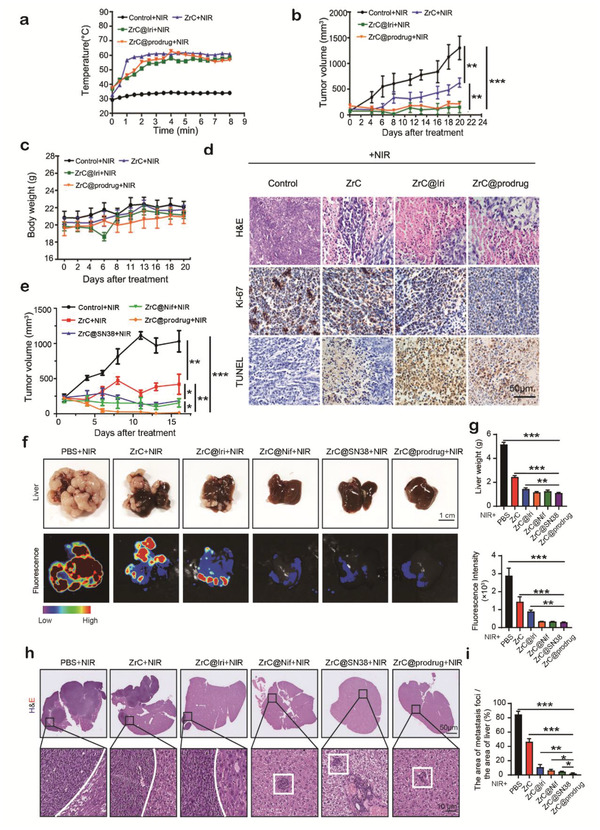
In vivo synergistic inhibition of tumor growth with ZrC@prodrug. a) Temperature curves at the tumor site with liver cancer model after different treatment (control+NIR, PEGylated ZrC+NIR, ZrC@Iri+NIR, and ZrC@prodrug+NIR) at different time intervals (1 W cm−2, 8 min). b) Time‐dependent tumor growth and c) body‐weight curves (n = 5, mean ± SD) after different treatments in SMMC‐7721‐induced subcutaneous liver cancer models. The NIR treatments were performed twice after 7 days. d) H&E staining, antigen Ki‐67 immunofluorescence, and TUNEL staining for pathological changes in tumor tissues. e) Time‐dependent tumor growth in Hepa1‐6‐induced subcutaneous liver cancer models in C57BL/6 mice with different treatments. f) 2 weeks later after different treatments (control+NIR, PEGylated ZrC+NIR, ZrC@Iri+NIR, ZrC@Nif+NIR, ZrC@SN38+NIR, and ZrC@prodrug+NIR), images of tumors in liver. g) Quantification of liver weight and fluorescence intensity in liver after various treatments. h) H&E staining in liver after various treatments. i) Percentage (%) of the area of metastasis loci in liver tissues after various treatments.
