Figure 1. Interspecies assessment of transcriptional signatures in MDD and CSV, SI and CSDS in mice.
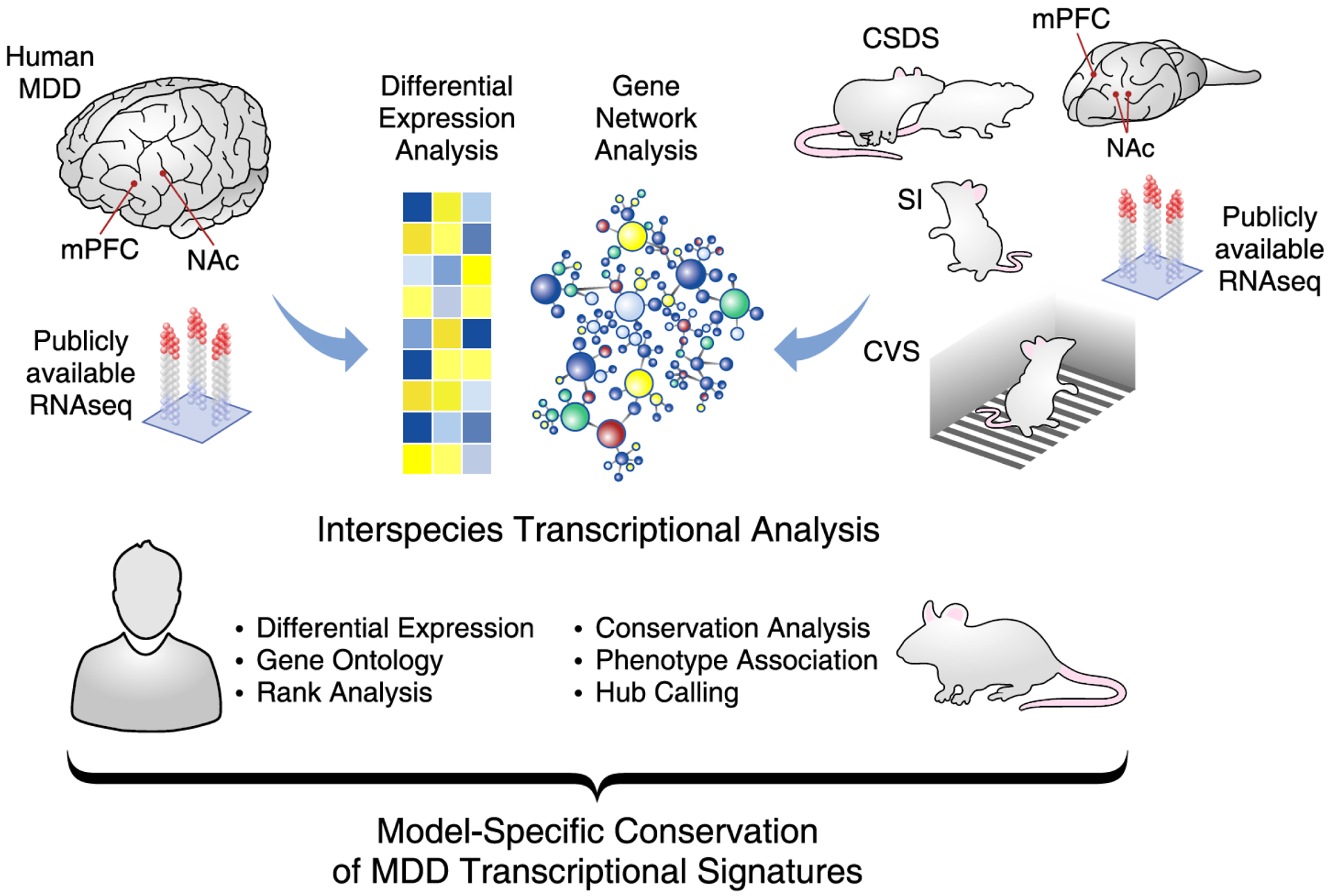
Publically available RNAseq data were obtained from cohorts of human major depressive disorder (MDD) and three mouse models of depressive-like behavior. These mouse models included the chronic variable stress (CVS), prolonged social isolation (SI) and chronic social defeat stress (CSDS) paradigms. Differential expression and weighted gene coexpression network analyses (WGCNA) were performed on each cohort by brain regions, including the medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC) and nucleus accumbens (NAc). Results from these analyses were combined and consistently compared across species. With these dataset, additional analyses including gene ontology overlap, hypergeometric rank, interspecies network conservation, phenotype association and hub calling analyses were performed. The final results allowed to catalogue the capacity of each mouse models to reproduce the transcriptional signatures relevant to MDD across different regions of the human brain.
