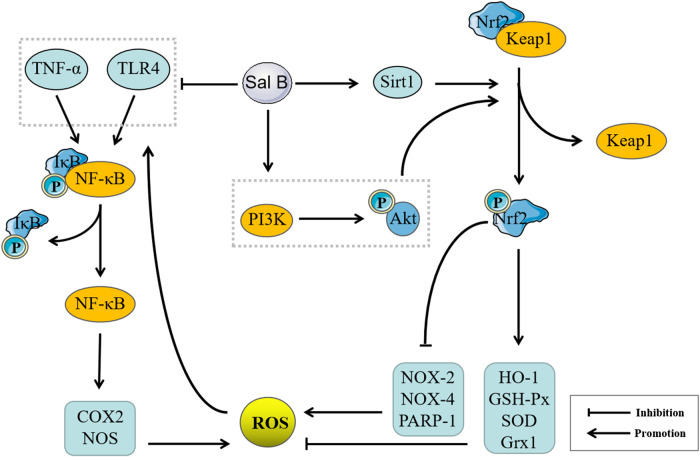
FIGURE 4.
Pharmacological mechanisms of Salvianolic acid B (Sal B) based on antioxidant effect. Sal B can inhibit the expressions of Tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, Cyclooxygenase (COX2) and NADPH oxidase (NOS) by inhibiting TNF-α/Nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) and Toll-like receptor (TLR4)/NF-κ-B pathways, and promote the expression of antioxidant enzymes such as Heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1), NQOD, Superoxide dismutase (SOD) and inhibit the expression of oxidases such as NOX-2, NOX-4, Poly (ADP-ribozyme) polymerase 1 (PARP-1) by the Nuclear factor E2-related factor 2/Kelch-like ECH-related protein 1 pathway, and then inhibit Reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation, improve inflammation, cell apoptosis, autophagy, fibrosis, microcirculation disorders, and stem cell proliferation and differentiation.