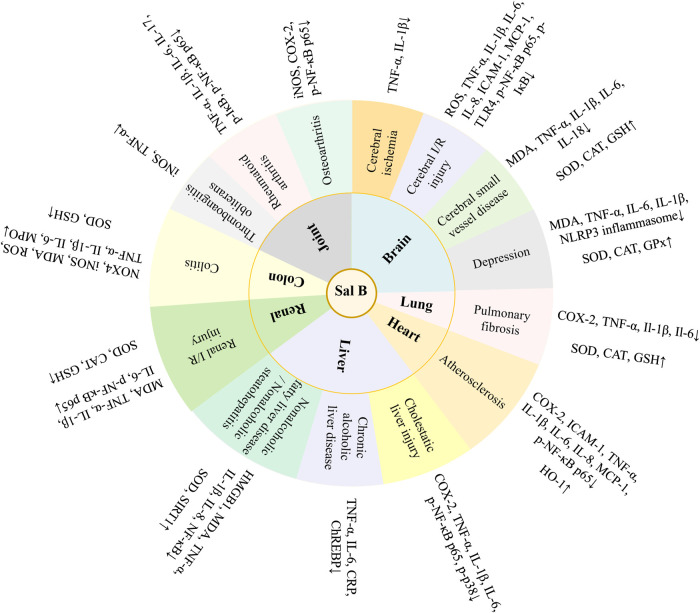
FIGURE 5.
Mechanisms of Salvianolic acid B (Sal B) in different chronic inflammatory diseases. In addition to increasing the expression of antioxidant enzymes such as Superoxide dismutase (SOD), CAT, GSH, and reducing the expression of oxidative enzymes such as Cyclooxygenase (COX-2), NADPH oxidase (NOX)-4, iNOS to inhibit the generation of Reactive oxygen species (ROS) and malondialdehyde (MDA), Sal B has been shown to improve chronic inflammation in a variety of disease models, suggesting that its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects are closely related.