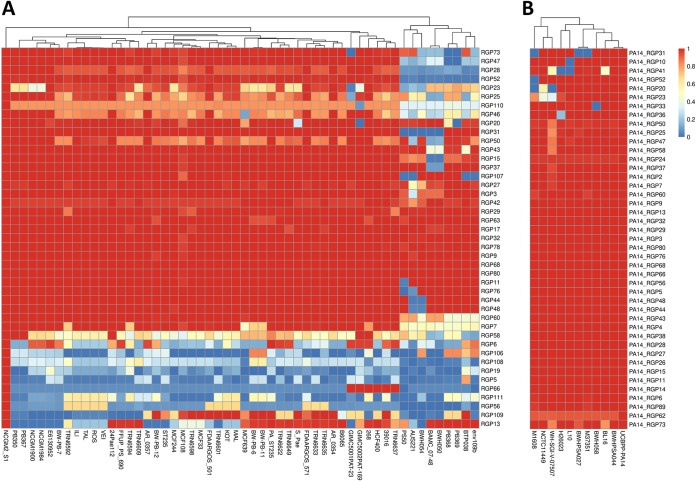
FIG 2.
Compositions of the accessory genomes of P. aeruginosa ST235 and ST253 strains. (A) The heat map shows the compositions of the accessory genomes in terms of RGPs of ST235 (F46D) isolates as well as of unrelated sequence types with a similar hexadecimal code. The dendrogram indicates that the ST235 isolates (left) are distinct from other sequence types (right outermost group of nine strains: ST205, AUS221; ST313, BAMC_07-48 and BWH050; ST319, PB368 and PB369; ST377, PS50; ST815, env109B; ST823, BTP038; ST830, BWH054) by their composition of accessory elements. The heat map depicts seven yet undescribed RGPs which were designated RGP106 to RGP112. Genome coordinates are given in Data Set S8 in the supplemental material. (B) The heat map shows the compositions of the accessory genomes in terms of RGPs in ST253 isolates whose genomes are represented in databases by less than 100 contigs. The ST253 variants of hexadecimal code D421 and D021 differ from each other by the presence and absence of RGP31. The barcode indicates the sequence similarity with the respective RGP of reference strains NCGM2.S1 (A) and PA14 (B).