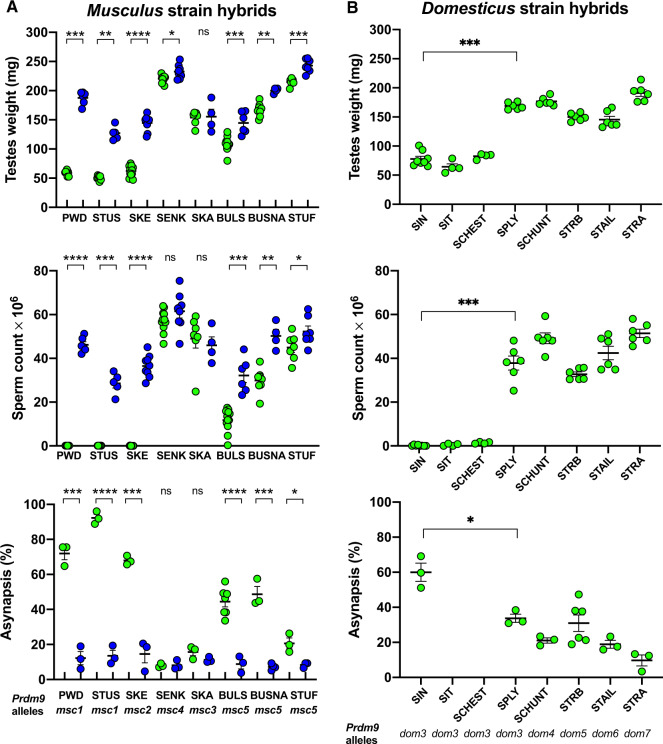
Fig. 4.
Fertility phenotypes and chromosome pairing of intersubspecific mouse hybrids. (A) Hybrids from crosses of musculus wild-derived inbred strain males and B6.DX1s (green circles) or B6.DX1s. Prdm9dom2H “humanized” domesticus females (blue circles). Only Prdm9msc1 and related Prdm9msc2 alleles support high asynapsis and full meiotic arrest or quasi sterility. The Prdm9 control of fertility phenotypes is shown by improved meiotic chromosome pairing and fertility parameters in hybrids carrying humanized alleles compared with the Prdm9dom2 allele. (B) Hybrids of PWD musculus females and wild-derived domesticus males. All wild-derived strains that carry the Prdm9dom3 allele except for SPLY, produced sterile hybrids. Asynapsis rate was significantly higher in sterile SIN hybrids than in fertile SPLY carrying the same Prdm9dom3 allele. Significance of fertility improvement caused by the humanized Prdm9 allele was evaluated by Mann–Whitney U test for testes weight and sperm count and by unpaired two-tailed t-test for asynapsis. P values <0.0001****, 0.0001–0.001***, 0.001–0.01**, 0.01–0.05*, >0.05 ns.