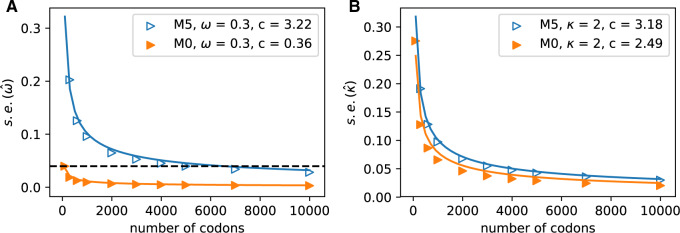
Figure 4.
Increasing the number of columns allows us to quantify how much information is retained in amino acid sequences (M5) relative to codon sequences (M0). The median standard errors of A)  and B)
and B)  decrease for both models as codons are added. The dashed horizontal line in a) indicates the observed median standard error of
decrease for both models as codons are added. The dashed horizontal line in a) indicates the observed median standard error of  for 100 codons under M0, and illustrates that M5 requires a substantially longer alignment to reach a comparable standard error. Fitting functions of the form
for 100 codons under M0, and illustrates that M5 requires a substantially longer alignment to reach a comparable standard error. Fitting functions of the form 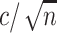 to the median standard errors, with
to the median standard errors, with 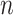 equaling the number of alignment columns, allows us to quantify the difference in information content. Equating
equaling the number of alignment columns, allows us to quantify the difference in information content. Equating 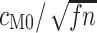 with
with 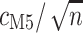 indicates equivalent information content for
indicates equivalent information content for 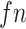 codons in M0 and
codons in M0 and 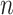 codons in M5: hence M5 recovers a fraction
codons in M5: hence M5 recovers a fraction 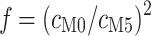 of the information available to M0. Alternatively, M5 has lost 100(1
of the information available to M0. Alternatively, M5 has lost 100(1 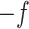 )% of the information available to M0.
)% of the information available to M0.