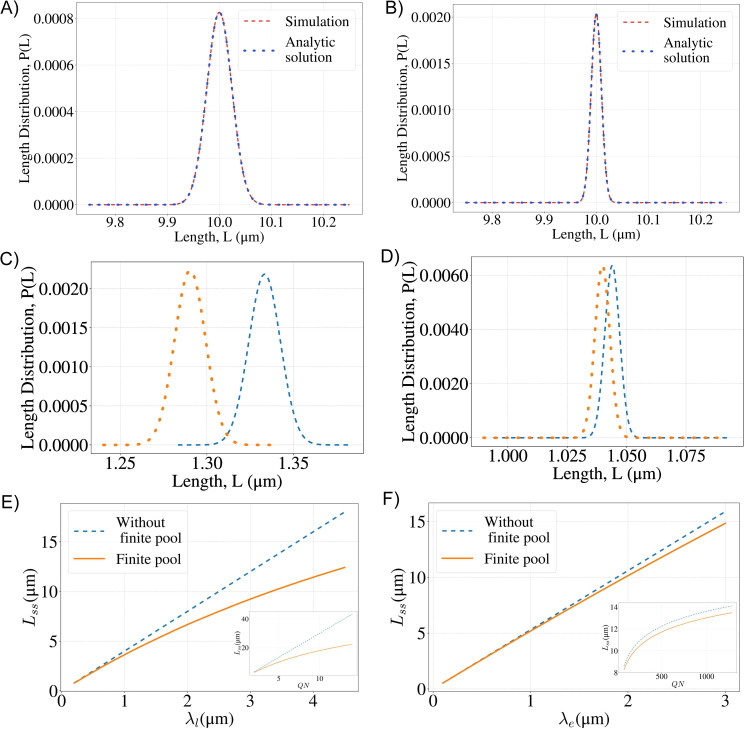
Fig 3. Effect of a finite monomer pool on control of filament lengths.
A,B Marginal distributions of the filament lengths for the linear (A) and the exponential (B) gradient model with finite monomer pool. Simulation results are plotted together with Eqs (15) and (17). C,D Comparison of length distributions for the linear (C) and exponential (D) gradient models when the monomer pool is large versus infinite, when only a small fraction (~2%) of monomers is in filaments. In both plots, the orange dashed curve represents the finite pool model and the light blue dashed curve represents the large pool limit. E, F. The steady state lengths (Lss) for the large monomer pool case (light blue) and the finite pool case (orange) for different values of the length scale of the gradient. Inset: steady state length for different values of QN while keeping N and λ fixed.(E)-linear gradient model, (F)–exponential gradient model. Parameters: N = 2×106. For A: QN = 5, λl = 6.66×104 (in monomer units); B: QN = 200, λe = 3.94×104 (in monomer units); C: QN = 5, λl = 6.66×103 (in monomer units); D: QN = 200, λe = 3.94×103 (in monomer units); E. QN = 5; Inset: λl = 6.66×104 F: QN = 200. Inset: λe = 3.94×103. (20,000 monomer units is one micron).