Fig. 1. Blockage of de novo polyamine biosynthesis suppresses T cell proliferation and reduces viability in vitro.
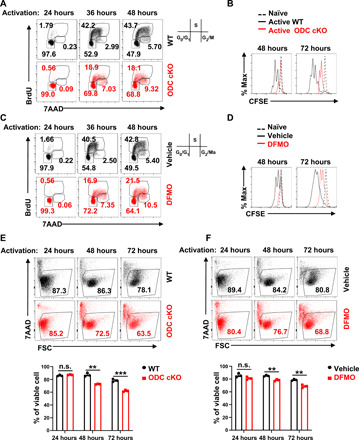
(A and C) Cell cycle of activated CD4+ T cells at 24, 36, and 48 hours with indicated genotypes or treatments was analyzed by using BrdU and 7AAD staining; the numbers indicate the percentage of cells in each cell cycle stage. Data represent three independent experiments. (B and D) Cell proliferation of naïve and activated CD4+ T cells at 48 and 72 hours with indicated genotypes or treatments was determined by CFSE dilution. Data represent six independent experiments. (E and F) Cell viability of activated CD4+ T cells at 24, 48, and 72 hours with indicated genotypes or treatments was assessed by 7AAD staining. Top panel is the representative dot plot, and bottom panel is the statistical analysis (means ± SEM). FSC, forward scatter. Data represent three independent experiments, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 compared with WT, one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA). n.s., not significant.
