Fig. 1. Mature, but not precursor, microRNAome is suppressed in glioblastomas and GSCs.
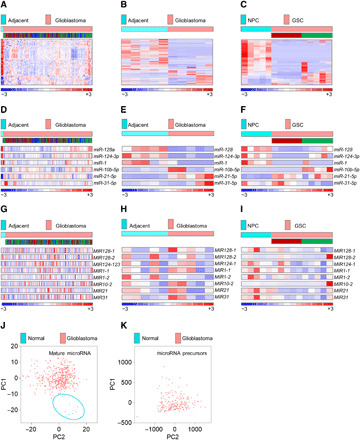
(A) Mature microRNAome in patients with glioblastoma (n = 490) versus healthy individuals (n = 11), based on 535 microRNAs in the TCGA database. The subtype identity: red, mesenchymal; blue, classical; green, proneural. (B and C) Mature microRNAome in glioblastoma tissue versus adjacent, nonpathological brain (n = 5 each) (B), and in GSCs (n = 5 per subtype) versus NPCs (n = 5) (C) based on 581 and 605 of 799 microRNAs by nCounter NanoString platform. GSC’s subtype identity is shown (red, mesenchymal; green, proneural). (D) Selected mature microRNAs in patients with glioblastoma (n = 490) versus healthy individuals (n = 11), based on the TCGA database. For the subtype identity, see (A). (E and F) Selected mature microRNAs in glioblastoma tissue versus adjacent, nonpathological brain (n = 5 each) (E), and in GSCs (n = 5 per subtype) versus NPCs (n = 5) (F), based on nCounter NanoString platform. For GSC’s subtype identity, see (B) and (C). (G) Selected microRNA precursors in patients with glioblastoma (n = 195) versus healthy individuals (n = 10), based on the TCGA database. For the subtype identity, see (A). (H and I) Selected microRNA precursors in glioblastoma tissue versus adjacent, nonpathological brain (n = 5 each) (H), and in GSCs (n = 5 per subtype) versus NPCs (n = 5) (I), based on custom NanoString precursor platform. For GSC’s subtype identity, see (B) and (C). (J and K) Mature microRNAome but not microRNA precursors distinguish between patients with glioblastoma and healthy individuals. PCA of mature (J) and precursors (K) microRNA in patients with glioblastoma (red dots, n = 490 and n = 205) versus healthy individuals (blue dots, n = 10) [(J) and (K), respectively].
