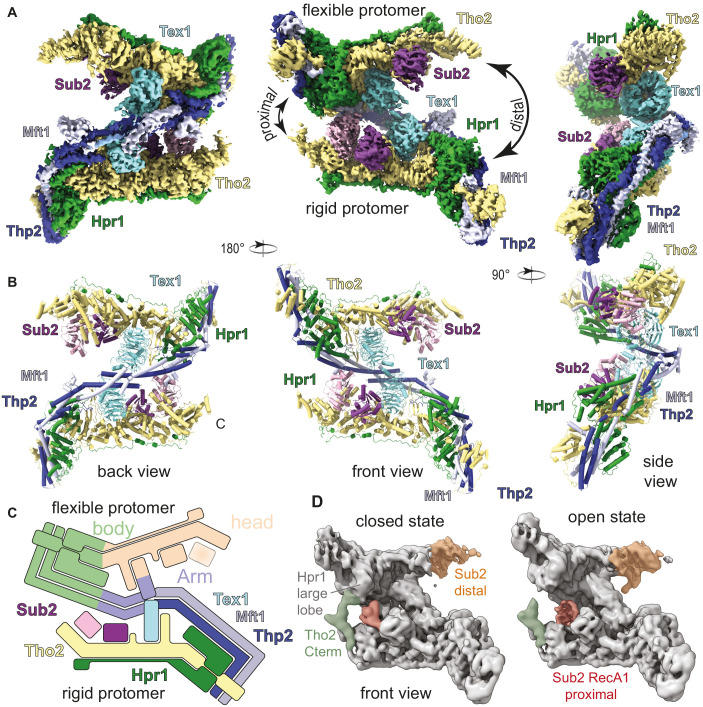
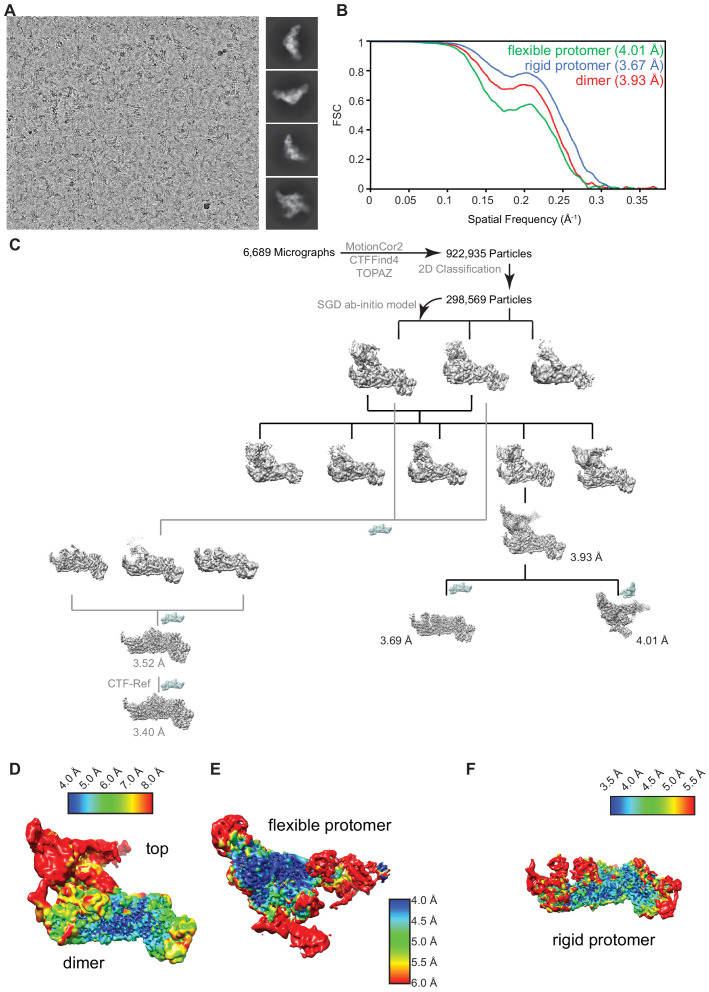
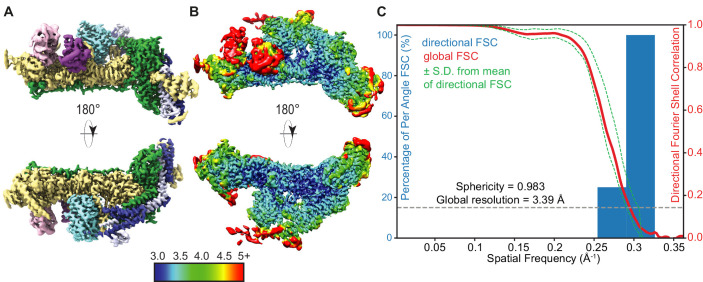
Figure 2. Cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) reconstruction of Saccharomyces cerevisiae THO-Sub2 homodimer.
(A) Segmented cryo-EM reconstruction of the THO-Sub2 dimer. Three different views are shown; proteins and domains are colored as in Figure 1A. Features discussed in the text are indicated, including the proximal and distal sides of the asymmetric homodimer, the rigid and flexible protomers, as well as the ‘head and ‘body’ of each protomer. (B) Cartoon representation of the structure, shown in the same orientations and colors. Helices are rendered as solid cylinders. (C) Schematic representation of the THO-Sub2 complex architecture based on the cryo-EM structure. (D) Two frames of the raw cryo-EM data outputs from the variance analysis shown in Video 1. The Tho2 C-termini of the two protomers are shown in orange and green. Different conformations are adopted as the dimer switches the proximal and distal sides.