Figure 3.
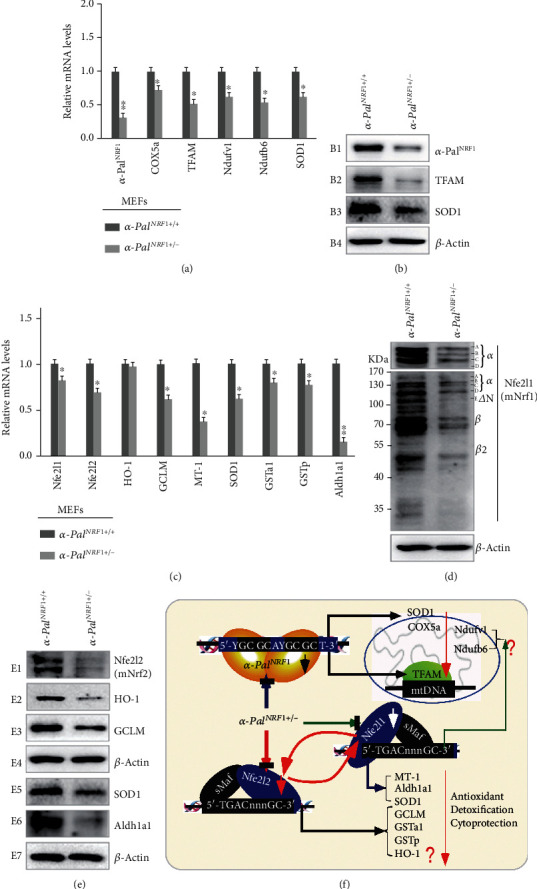
Distinct effects of mouse α-palNRF1+/- on the expression of Nfe2l1, Nfe2l2, TFAM, and related genes. (a) Altered mRNA levels of α-palNRF1, COX5a, TFAM, Ndufv1, Ndufb6, and SOD1 in α-palNRF1+/- MEFs were compared with their equivalents measured from wild-type (α-palNRF1+/+) cells. The data are shown as mean ± SEM (n = 3 × 3) with significant decreases (∗p < 0.01, ∗∗p < 0.001). (b) Significant changes in α-PalNRF1, TFAM, and SOD1 proteins were detected by Western blotting of α-palNRF1+/- and α-palNRF1+/+ MEFs. (c) Changes in basal mRNA levels of Nfe2l1 and Nfe2l2, as well as indicated antioxidant genes, were determined by real-time qPCR of α-palNRF1+/- MEFs, when compared with α-palNRF1+/+ MEFs. The results are shown as mean ± SEM (n = 3 × 3) with significant decreases (∗p < 0.01, ∗∗p < 0.001). (d) Altered abundances of distinct Nfe2l1 isoforms in between α-palNRF1+/- and α-palNRF1+/+ MEFs were also visualized. (e) Altered protein levels of Nfe2l2 and the indicated antioxidant enzymes, such as HO-1, GCLM, SOD1, and Aldh1a1, were further unraveled by Western blotting of α-palNRF1+/- and α-palNRF1+/+ MEFs. (f) A model is proposed to explain distinct effects of α-palNRF1+/- on the nuclear-to-mitochondrial respiratory and antioxidant genes in MEFs.
