Figure 4.
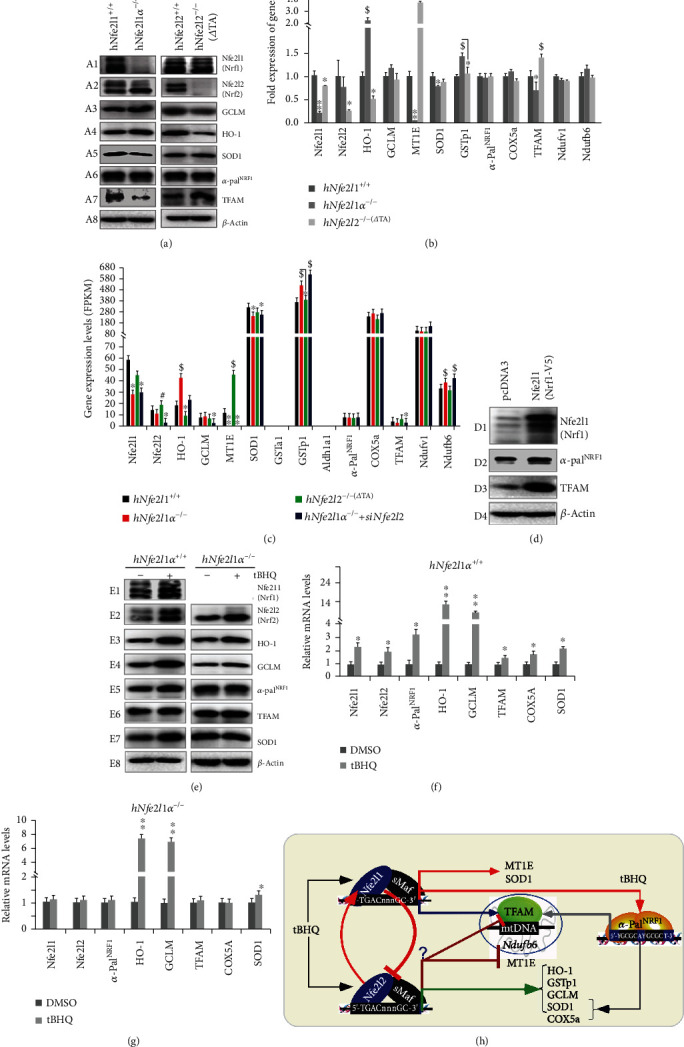
Distinct changes of human α-PalNRF1 and TFAM in HepG2-derived hNfe2l1α−/− and hNfe2l2−/− cell lines. (a) Distinct protein levels of human Nfe2l1, Nfe2l2, α-PalNRF1, and TFAM as well as other relevant proteins were determined by Western blotting of hNfe2l1α−/−, hNfe2l2−/−, and wild-type HepG2 cells. (b) Basal mRNA expression levels of Nfe2l1, Nfe2l2, α-PalNRF1, TFAM, and other indicated genes were examined by real-time qPCR of hNfe2l1α−/−, hNfe2l2−/−, and wild-type HepG2 cells. The resultant data are shown as mean ± SEM (n = 3 × 3) with significant decreases (∗p < 0.01, ∗∗p < 0.001) or significant increases ($, p < 0.01; $$, p < 0.001). (c) The FPKM (Reads Per Kilobase per Million mapped reads) value of Nfe2l1, Nfe2l2, α-PalNRF1, TFAM, and other indicated genes were obtained by RNA-sequencing of hNfe2l1α−/−, hNfe2l2−/−, hNfe2l1α−/−+siNfe2l2, and hNfe2l1/2+/+. (d) Different protein levels of Nfe2l1, α-PalNRF1, and TFAM were examined in HepG2 cells that had been transfected with an hNfe2l1 expression construct or empty pcDNA3.1. (e) Distinct inducible alterations in abundances of Nfe2l1, Nfe2l2, α-PalNRF1, TFAM, HO-1, GCLM, and SOD1 were determined by Western blotting of hNfe2l1α+/+ or hNfe2l1α−/− that had been or not been treated with 50μmol/L tBHQ. (f, g) Distinct inducible mRNA levels of Nfe2l1, Nfe2l2, α-PalNRF1, HO-1, GCLM, TFAM, COX5a, and SOD1 were revealed by real-time qPCR of between tBHQ-stimulated lines of hNfe2l1α+/+ cells (f) and hNfe2l1α−/− cells (g). The resultant data are shown as mean ± SEM (n = 3 × 3) with significant increases (∗p < 0.01, ∗∗p < 0.001). (h) A model is assumed to present cross-talks between human Nfe2l1 and Nfe2l2, along with distinct effects on human α-PalNRF1, TFAM, and other gene expression, particularly upon stimulation by tBHQ.
