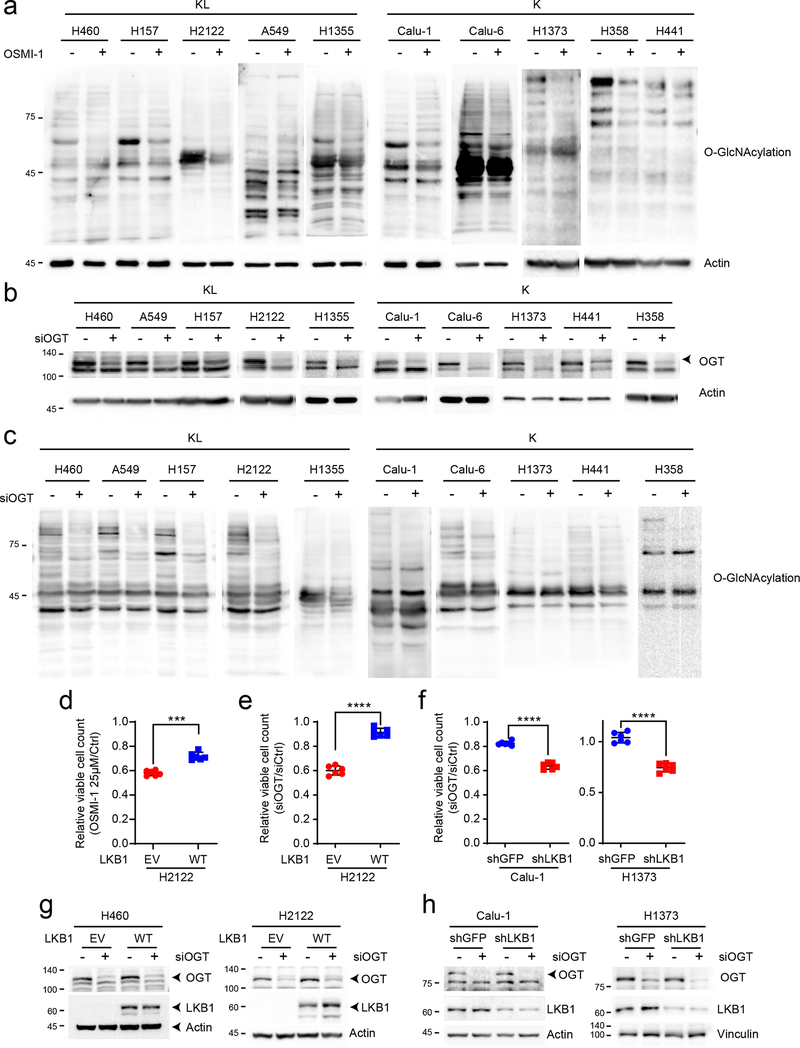
Extended Data Fig. 5. KL cells are sensitive to inhibition of the HBP.
a, Effect of OSMI-1 treatment on global O-GlcNAcylation of K and KL cells. b, Abundance of OGT protein in K and KL cell lines transfected with a control siRNA or siRNA directed against OGT. Actin is used as a loading control. c, Effect of OGT silencing on global O-GlcNAcylation of K and KL cells. d, Relative viability of EV and LKB1-WT expressing H2122 cells following a 72hr exposure to OSMI-1 (25μM). e, Relative viability of EV and LKB1-WT expressing H2122 cells to OGT silencing for 96hr. f, Relative viability of shGFP and shLKB1-expressing Calu-1 (Left) and H1373 (Right) cells to OGT silencing for 96hr. g and h, Abundance of OGT protein in EV and LKB1 expressing KL cells (H460 and H2122) (g) and shGFP and shLKB1 expressing K cells (Calu-1 and H1373) (h) transfected with a control siRNA or siRNA directed against OGT. Actin is used as a loading control except H1373 (Vinculin is used as a loading control). Statistical significance was assessed using two-tailed Student’s t-tests. ***p<0.001; ****p<0.0001. Cell viability assays were repeated twice, and all Western blots were repeated three times or more.