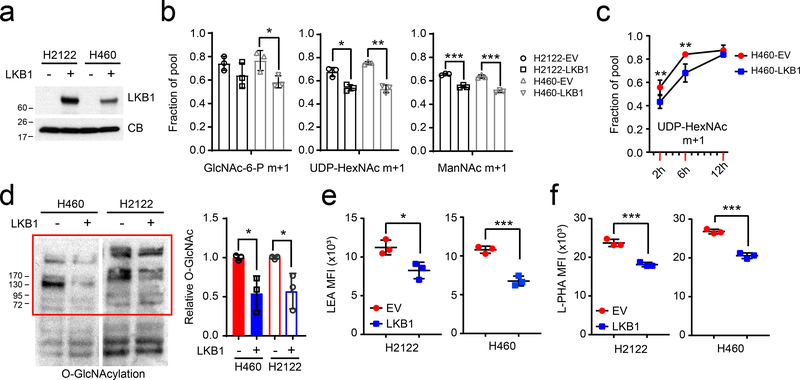
Figure 3. LKB1 regulates the hexosamine biosynthesis pathway.
a, LKB1 re-expression in H460 and H2122, two KL cells. Cyclophilin B (CB) is used as loading control. b, 15N labeling in GlcNAc-6-P, UDP-HexNAc and ManNAc in empty vector (EV) control and wildtype LKB1 (LKB1) expressing H460 and H2122 cells cultured with [γ−15N]glutamine. c, Time-course of 15N labeling in UDP-HexNAc in EV and LKB1 expressing H460 cells cultured with [γ−15N]glutamine. d, Left, Global O-GlcNAcylation in EV and LKB1 expressing H460 and H2122 cells. Right, Relative intensity of O-GlcNAcylation (in red bracket) to a loading control (cyclophilin B, CB). e, Cell surface LEA lectin binding in EV and LKB1-expressing H460 and H2122 cells was measured by flow cytometry. f, Cell surface L-PHA lectin binding in EV and LKB1 expressing H460 and H2122 cells was measured by flow cytometry. Data in b and c are the average and SD of three independent cultures. In b,e,f, statistical significance was assessed using two-tailed Student’s t-test. In c, to calculate significance on repeated measurements over time, two-way ANOVA was used. Stable isotope experiments and O-GlcNAcylation western blotting were repeated twice. All other experiments were repeated three times or more. *p<0.05;**p<0.01; ***p<0.001.