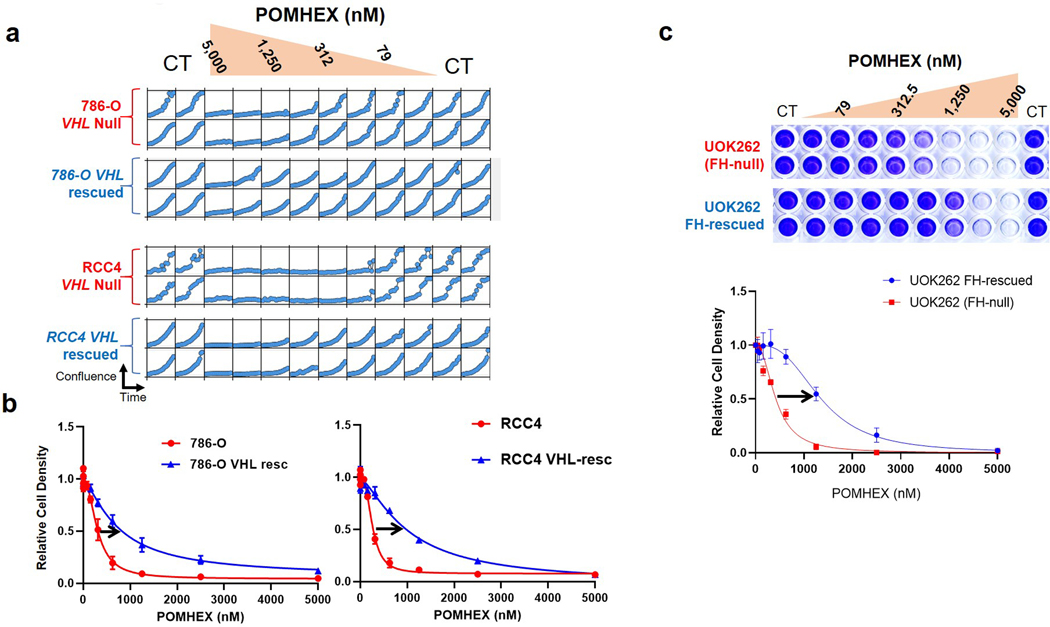
Extended Data Fig. 7. Utility of Enolase inhibitors beyond cancers with ENO1-deletions.
Hyperactivation of HIF by loss of VHL tumor suppressor gene has been reported to sensitize cells to glycolysis inhibition12. a. Proliferation of renal clear cell carcinoma cell lines that lack functional VHL (786-O and RCC4, red) and isogenic rescued cell lines re-expressing VHL (blue) was followed by Incucyte live cell imager (x-axis, time; y-cell confluence) in response to POMHEX treatment. Each box represents one biological replicates. VHL-deleted parental lines showed 4- to 8-fold greater sensitivity than isogenic rescued VHL lines. b. Cell density quantified by crystal violet for the same cell lines corroborates Incucyte live imaging data (N = 4 biological replicates, with +/− S.E.M.). IC50 for POMHEX in the RCC4 line is ~250 nM and 1,000 nM in the isogenic rescued line. TCA-cycle deficiency and defective oxidative phosphorylation by loss of function of Fumarase (FH) increase reliance on glycolysis and sensitize to glucose deprivation11. c. Likewise, the FH-null renal carcinoma cell line, UOK262, (red) shows dramatically higher sensitivity to the Enolase inhibitor POMHEX than isogenic FH-rescued cell line control (blue). Cell density in response to POMHEX treatment was quantified by crystal violet (N = 4 biological replicates, with +/− S.E.M.).