Figure 4: Injectable hydrogel approaches and in vivo efficacy.
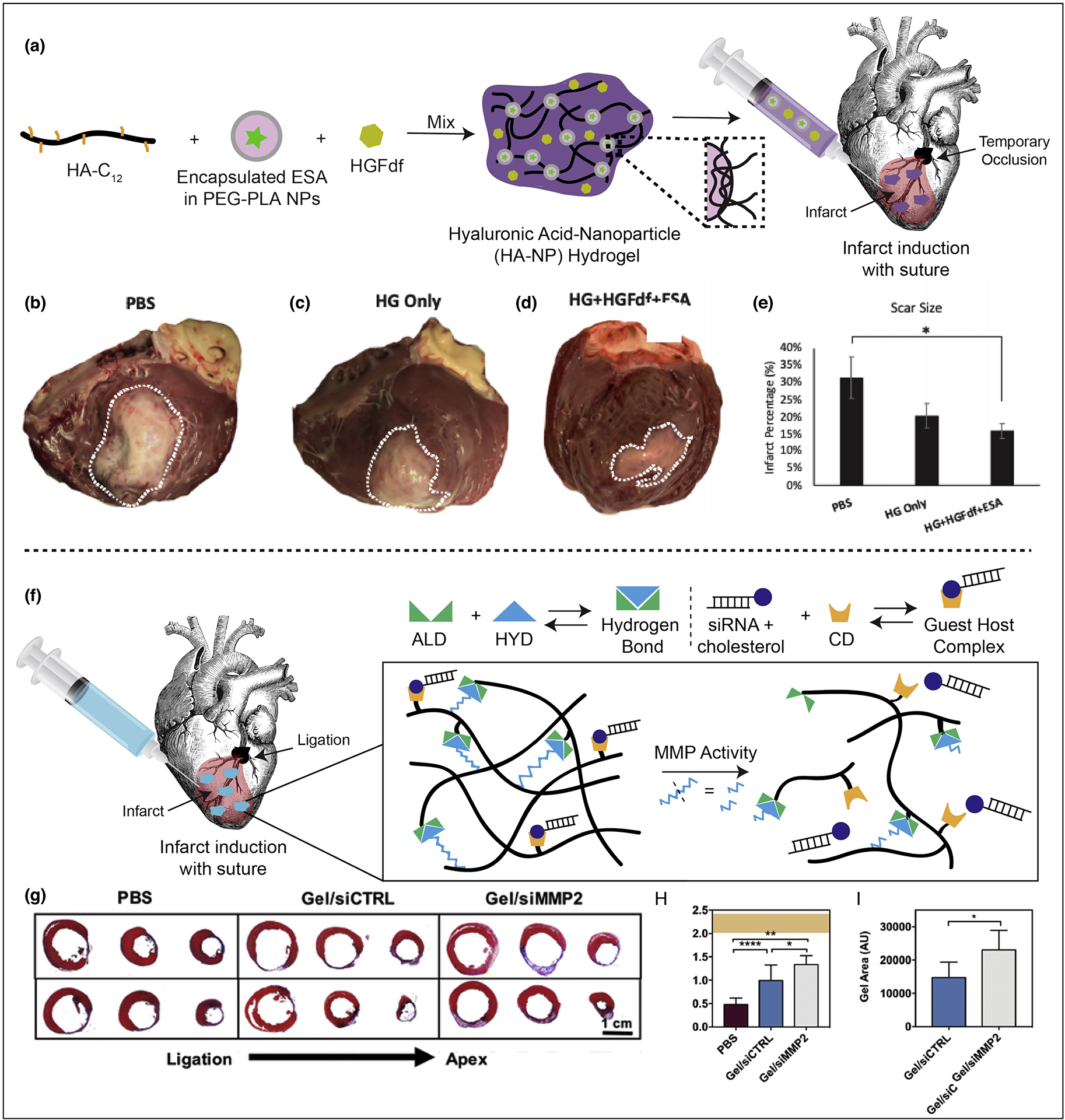
A. Demonstration of hydrogel formation with encapsulated cytokines. HA-NP hydrogel is composed of a hydrophobically-modified hyaluronic acid (HA) which is crosslinked by hydrophobic polyethyleneglycol block polylactic acid (PEGPLA) nanoparticles. The ESA is encapsulated into the nanoparticle phase and HGFdf is encapsulated into the aqueous phase of the hydrogel. B–E. Left ventricle infarct area. Hearts were explanted and opened longitudinally. The infarct was photographed for quantification and representative images of hearts from each group are presented. (B) PBS treated (C) HG only treated and (D) HG + HGFdf + ESA treated animals were evaluated. (E) HG + HGFdf + ESA demonstrated a significantly reduced infarct size compared to PBS animals and smaller average infarcts compared to HG only animals. ANOVA with a Bonferroni correction for multiple comparisons, *p < 0.05. F. Schematic demonstrating siRNA-cholesterol association with hydrogel via cholesterol/CD interactions and illustrating hydrogel erosion in response to MMPs. G. Representative Masson’s trichrome sections (3 representative sections from ligation to apex from left to right in 2 representative animals per group, 1 animal per row). H. Quantification of infarct thickness from Masson’s trichrome sections across three representative axial/transverse sections per animal (mean ± SD, *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ****p<0.001, PBS: n=6, gel/siCTRL: n=7, gel/siMMP2: n=6) and presented in context of healthy controls (orange, mean ± SD, n=7). I. Quantification of hydrogel area from Masson’s trichrome sections across three representative axial/transverse sections per animal (mean ± SD, *p<0.05, PBS: n=6, gel/siCTRL: n=7, gel/siMMP2: n=6). Reproduced with edits and permissions from Elsevier.
