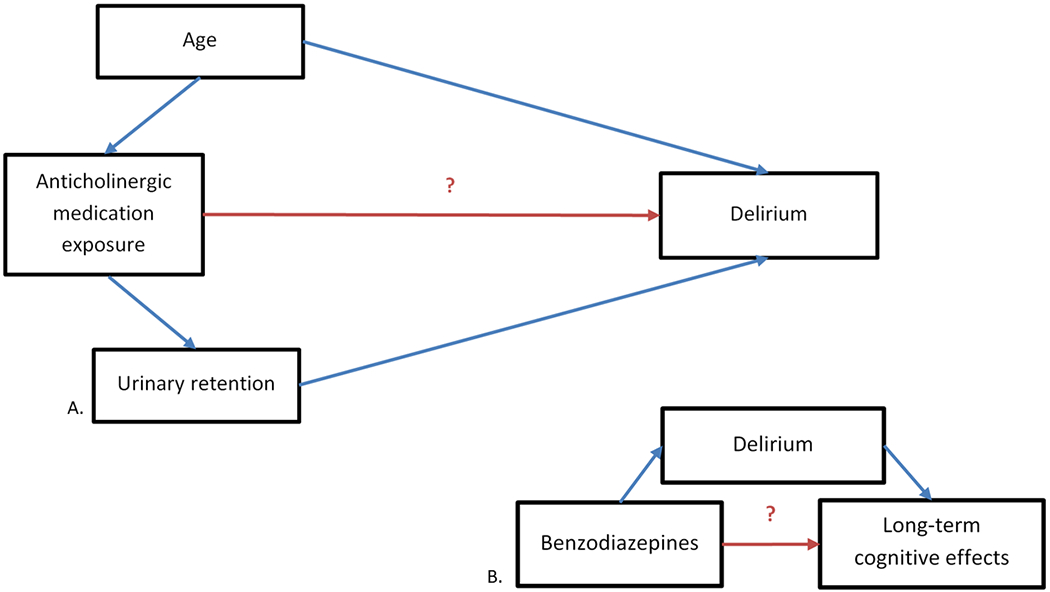
Part A. Diagram of the relationship between medication exposure and post-operative delirium. Part B. Simplified diagram of the potential association between benzodiazepines, delirium, and long-term cognitive effects. The head of the arrow indicates the direction of presumed causality. In this example, age is potentially causally-associated with anticholinergic medication exposure and with delirium, making it a confounder. Urinary retention potentially lies on the causal pathway between anticholinergic medication exposure and delirium, and is therefore excluded from the model, as controlling for it would mask the true association between anticholinergic activity and delirium.
