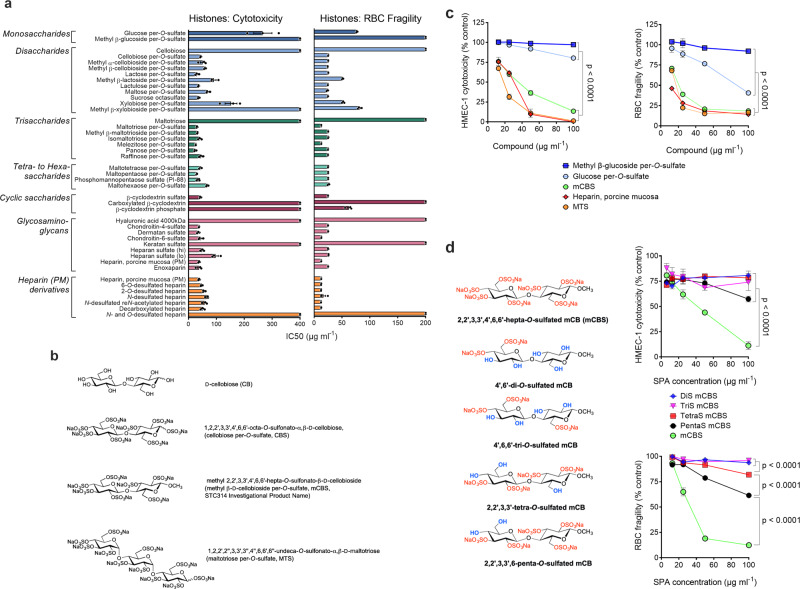
Fig. 1. Polyanions inhibit histone-mediated endothelial cell cytotoxicity and RBC fragility with minimal structural requirements for the activity identified.
a Human endothelial cells (HMEC-1) (left panel) or red blood cells (RBCs) (right panel) were incubated (1 h, 37 °C) with histones (400 μg ml−1) in the presence of different polyanion concentrations and IC50 values (mean of three separate determinations ± s.e.m.) for HMEC-1 cytotoxicity or RBC fragility determined. Heparan sulfate (lo) and (hi) represent low and highly sulfated heparan sulfate. b Chemical structures of compounds selected for future study. c Sulfated disaccharide mCBS has minimal structural requirements to approximate inhibitory effect of heparin on histone-mediated cytotoxicity and RBC fragility, the monosaccharides, methyl β-glucoside per-O-sulfate and glucose per-O-sulfate having little or no activity. d Effect of the level of sulfation of mCB (di-, tri-, tetra-, and penta-O-sulfated) on its ability to be an effective inhibitor of histone-mediated cytotoxicity and RBC fragility compared to fully sulfated (hepta-O-sulfated) mCBS. Data are presented as mean ± s.e.m. (n = 3) and analyzed by two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s correction for multiple comparisons. Source data are provided as a Source Data File.