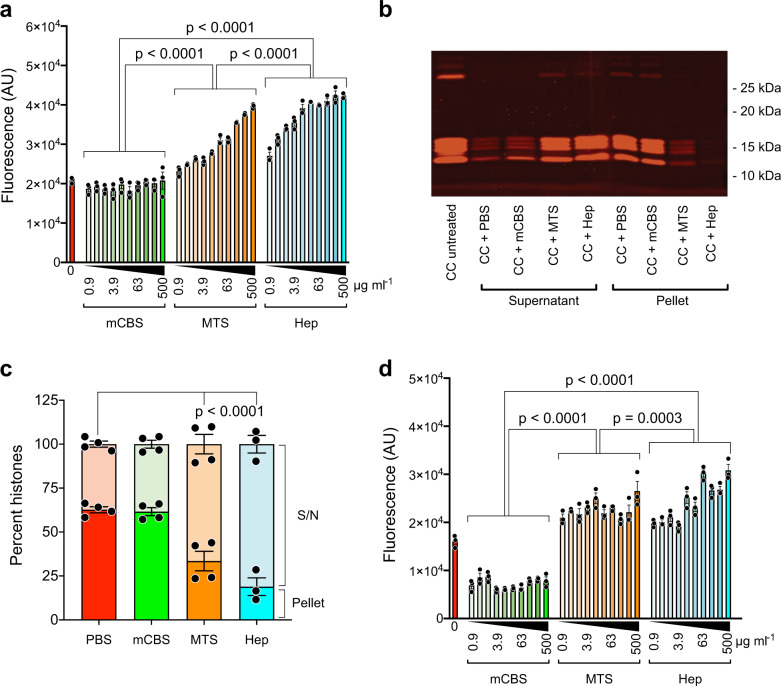
Fig. 8. Polyanion-induced changes in chromatin and NETs.
a Enhanced uptake of the fluorescent DNA-specific dye, Sytox Green, by chicken chromatin (CC) following exposure to the polyanions MTS and heparin, but not mCBS at concentrations ranging from 0.9 to 500 µg ml−1 (n = 3/treatment). Data suggest that MTS and heparin can displace histones from CC over a wide concentration range, whereas mCBS cannot. b CC exposed to 500 µg ml−1 of mCBS, MTS, and heparin, pelleted by centrifugation, and supernatants and pellets collected and run on SDS-PAGE. Representative data from one gel (137% normal size), confirming that MTS and heparin can displace histones from CC, whereas mCBS cannot. c Histogram including all the SDS-PAGE data and showing that MTS and heparin displace histones from CC, an effect that is significant (n = 4/treatment). d Sytox Green uptake by human NETs following incubation with mCBS, MTS, and heparin as in b above (n = 3/treatment). Data similar to that obtained with CC incubated with MTS and heparin. However, unlike CC, mCBS reduced Sytox Green uptake by NETs by ~50%, suggestive of NET stabilization. Solid circles are individual data points and are presented as mean ± s.e.m. and analyzed by two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s correction for multiple comparisons. Source data are provided as a Source Data File.