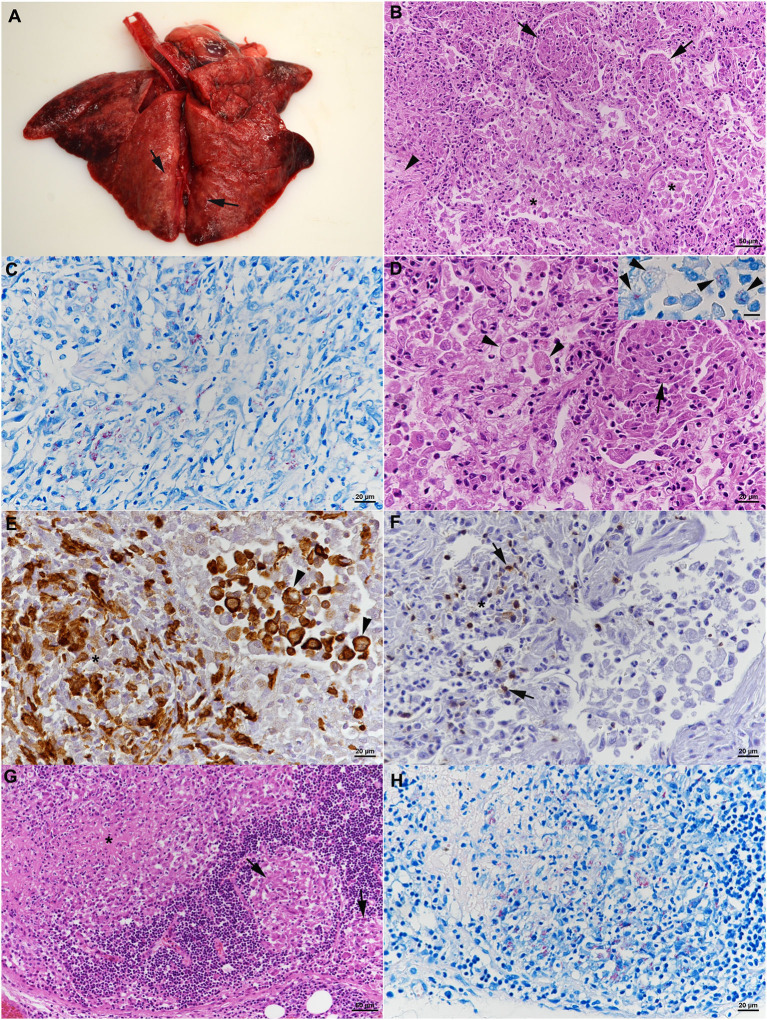
Figure 4.
Case 2, histological features. (A–F) Lungs. (A) Gross picture of the lungs after exenteration. All lung lobes appear consolidated, with focal nodular thickening of the parenchyma (arrows). (B) Severe pneumonia with multiple granulomatous infiltrates (arrows) and focal areas of fibrosis (arrowhead). Alveoli often contain macrophages as well (*). HE stain. Bar = 50 μm. (C) Numerous macrophages and epithelioid cells contain individual or bundles of acid fast bacilli (AFB). Ziehl Neelsen (ZN) stain. Bar = 20 μm. (D) Closer view of granulomatous infiltrate (arrow) and alveoli that are filled with desquamed vacuolated alveolar macrophages/type II pneumocytes (arrowheads) that also contain AFB (inset; ZN stain). HE stain. Bars = 20 μm. (E) The granulomatous infiltrates (*) are dominated by Iba-1+ macrophages/epithelioid cells. Staining of cells in the alveolar lumina shows that the majority are macrophages (Iba-1+). Bar = 20 μm. (F) T cells (CD3+) are found intermingled in small numbers in the granulomatous infiltrates. (G,H) Mandibular lymph node. (G) Cortex with focal granulomatous infiltrates (arrows) and a larger infiltrate toward the medulla, with central necrosis (*). HE stain. Bar = 50 μm. (H) Numerous macrophages/epithelioid cells in the infiltrates contain AFB. ZN stain. Bar = 20 μm.