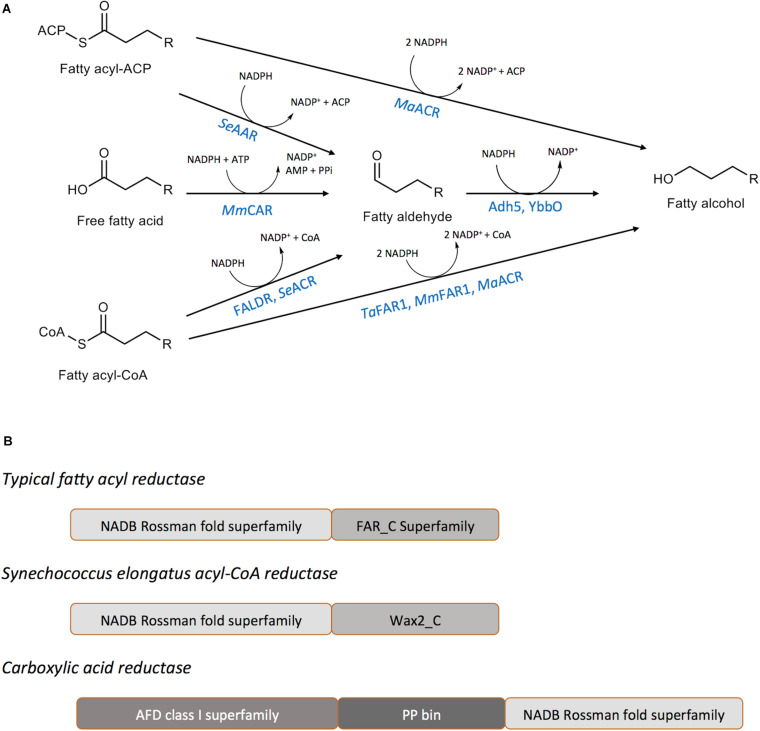
FIGURE 2.
Enzymes catalyzing fatty alcohol formation. (A) Reaction schemes for fatty alcohol synthesis from common precursors indicating the enzymes required and intermediates generated. MaFAR, Marinobacter aquaeolei VT8 acyl-CoA reductase; Adh5, S. cerevisiae alcohol dehydrogenase 5; YbbO, E. coli aldehyde reductase; MmCAR, Mycobacterium marinum carboxylic acid reductase; FALDR, fatty aldehyde forming reductase; TaFAR1, Tyto alba fatty acyl-CoA reductase 1; MmFAR1, Mus musculus fatty acyl-CoA reductase 1. (B) Domains of the common enzymes utilized for the production of fatty alcohols. Typical FARs and Synechococcus elongatus acyl-CoA reductase enzymes include an amino-terminal NAD(P)H/NAD(P)+ binding (NADB) Rossman fold domain. Carboxyl-terminal domains belong to either the FAR-C or WAX2-C super families that are common among short-chain reductases. Carboxylic acid reductase enzymes possess a large amino-terminal adenylate forming Class I superfamily domain (AFD), a central phosphopantetheine binding site (PP bin), and a carboxyl-terminal large NADB Rossman fold.