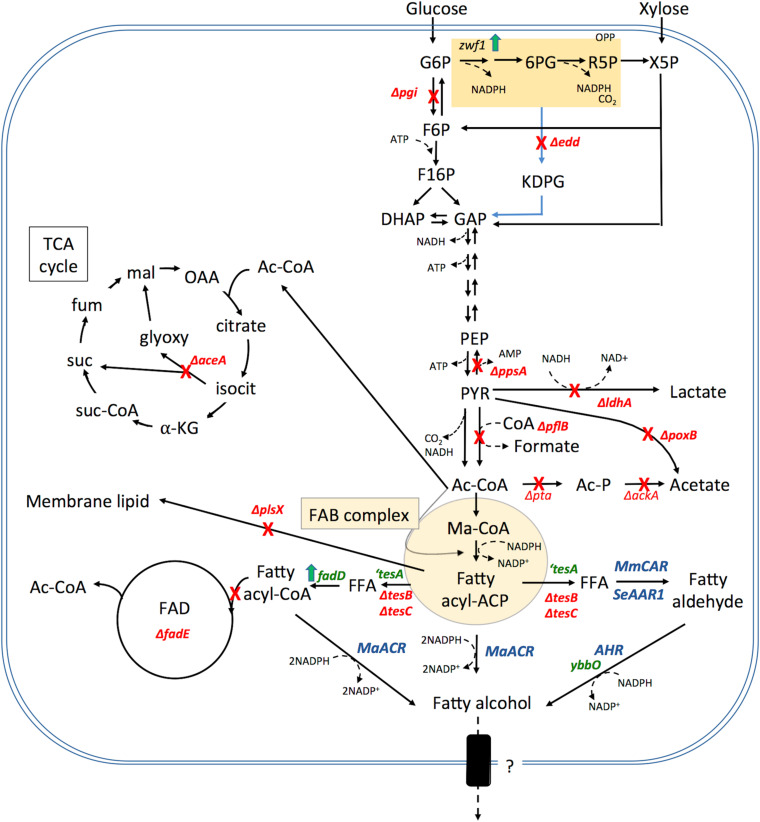
FIGURE 3.
Summary of metabolic engineering performed for fatty alcohol production in E. coli. Genes that have been effectively inactivated (shown in red), overexpressed (shown in green) and heterologous enzyme expression (shown in blue) that have resulted in increased fatty alcohol production in E. coli. Cofactors are noted in particularly salient positions but are omitted from others for clarity. Note: these genetic modifications have not necessarily been combined into a single production strain. Abbreviation and gene names used are: G6P, glucose-6-phosphate; 6PG, 6-phosphogluconate; R5P, ribulose-5-phosphate; X5P, Xylulose-5-phosphate; OPP, oxidative pentose phosphate pathway; F6P, fructose-6-phosphate; F16P, fructose-1,6-bisphosphate; DHAP, dihydroxyacetone phosphate; GAP, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate; PEP, phosphoenolpyruvate; PYR, pyruvate; Ac-CoA, acetyl Co-enzyme A; Ma-CoA, Malonyl CoA; KDPG, 2-Keto-3-deoxy-6-phosphogluconate; OAA, oxaloacetate; isocit, isocitrate; αKG, α-ketoglutarate; suc-CoA, succinyl-CoA; suc, succinate; fum, fumarate; mal, malate; glyoxy, glyoxylate; FFA, free fatty acid; Ac-P, acetyl phosphate; ACP, acyl carrier protein; FAB, fatty acid biosynthesis; FAD, fatty acid degradation; zwf1, Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase; pgi, phosphoglucose isomerase; edd, phosphogluconate dehydratase; ppsA, phosphoenolpyruvate synthetase; ldhA, lactate dehydrogenase; pflB, pyruvate formate lyase; poxB, pyruvate oxidase; ackA, acetate kinase; pta, phosphate acetyltransferase; tes, thioesterase; plsX, phosphate acetyltransferase involved in phospholipid metabolism; aceA, isocitrate lyase; ybbO, NADP+-dependent aldehyde reductase; AHR, aldehyde reductase; MmCAR, Mycobacterium marinum carboxylic acid reductase; SeAAR, Synechococcus elongatus acyl-CoA reductase; MaFAR, Marinobacter aquaeolei VT8 acyl-CoA reductase; fadD, long-chain-fatty-acid-CoA ligase; fadE, Acyl-CoA dehydrogenase.