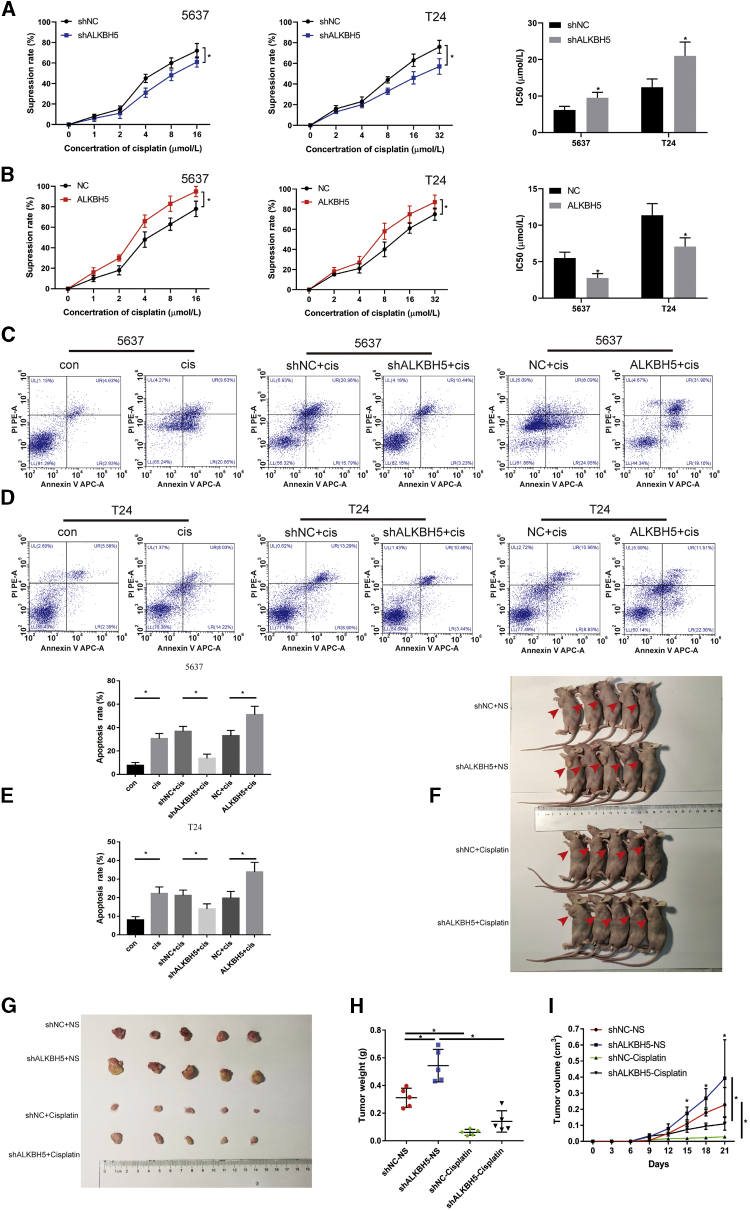
Figure 3.
ALKBH5 Increased Sensitivity to Cisplatin In Vivo and In Vitro
(A) Knockdown of ALKBH5 expression decreased the suppression rate of cisplatin and increased IC50 to cisplatin in 5637 and T24 cells by CCK-8. Data represent the mean ± SD from three independent experiments, ∗p < 0.05. (B) Overexpression of ALKBH5 expression increased the rate of cisplatin and decreased IC50 to cisplatin in 5637 and T24 cells by CCK-8. Data represent the mean ± SD from three independent experiments, ∗p < 0.05. (C–E) The percentage of apoptotic cells was increased after treatment with cisplatin for 48 h. Knockdown of ALKBH5 expression decreased the rate of cisplatin-induced apoptosis compared with control cells in 5637 and T24 cells, whereas overexpression of ALKBH5 increased the rate of cisplatin-induced apoptosis. Data represent the mean ± SD from three independent experiments. Student’s t test with two biological independent replicates was used to determine statistical significance, ∗p < 0.05. (F and G) Subcutaneous xenograft tumor model with ALKBH5 knockdown (shALKBH5) or control cells (shNC). Cisplatin or normal saline was injected intraperitoneally starting from day 7 of tumor inoculation. The red arrows indicate the location of the tumor. (H) Tumor weight was measured after 3 weeks from transplanting. Data represent the mean ± SD, ∗p < 0.05. (I) Tumor volume was measured every 3 days from transplanting. Data represent the mean ± SD, ∗p < 0.05.