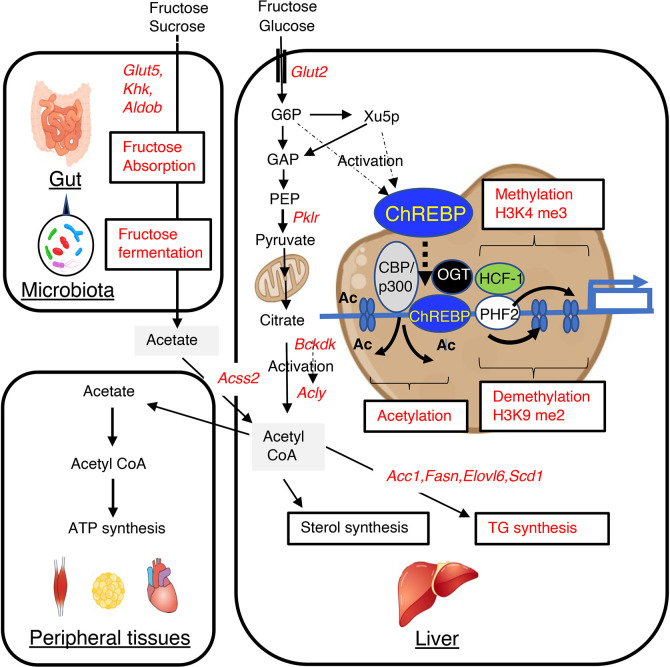
Figure 1.
High-fructose/high-sucrose diet-feeding causes an increase in de novo lipogenesis through the regulation of lipogenic gene expression and gut microbiota-derived acetate utilization. Fructose is normally absorbed and converted to glucose and lactate. Glucose, lactate, and a small amount of fructose enter the portal vein. In the liver, glucose and fructose activate ChREBP transcriptional activity through increases in the concentrations of glucose and fructose-derived metabolites, such as xylulose-5-phosphate and glucose-6-phosphate, and this results in greater expression of lipogenic genes, such as Acc1, Fasn, Elovl6, and Scd1. This higher expression causes the metabolism of glucose and fructose to generate acetyl CoA and fatty acyl CoA in the liver. Fructose that is not absorbed in the small intestine is absorbed in the colon and enters the portal vein. In the liver, acetate is converted to acetyl CoA by acyl-coenzyme A synthetase short-chain family member 2 (encoded by Acss2), and this is used for fatty acyl CoA synthesis, sterol synthesis, and histone acetylation. ChREBP transcription activity is also regulated by acetyl CoA and uridine diphosphate-N-acetylglucosamine, through acetylation and O-GlcNAcylation, respectively. These substances are involved in epigenic regulation, such as histone acetylation and histone methylation. GLUT5, glucose transporter 5; KHK, ketohexokinase; ALDOB, aldolase B; GLUT2, glucose transporter 2; PKLR, liver-type pyruvate kinase; ACSS2, acyl-coenzyme A synthetase short-chain family member 2; G6P, glucose 6-phosphate; Xu5P, xylulose 5-phosphate; ACLY, ATP citrate lyase; ACC1, acetyl CoA carboxylase; FASN, fatty acid synthase; ELOVL6, fatty acid elongase 6; SCD1, stearyl CoA desaturase; BCKDK, branched-chain ketoacid dehydrogenase kinase; CBP, CREB binding protein; OGT, O-linked N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc) transferase; HCF-1, host cell factor-1; PHF2, plant homeodomain finger 2; H3K4me3, trimethylated H3K4; H3K9me2, dimethylated H3K9.