Figure 2.
Anti-lymphoma activity of NQBS
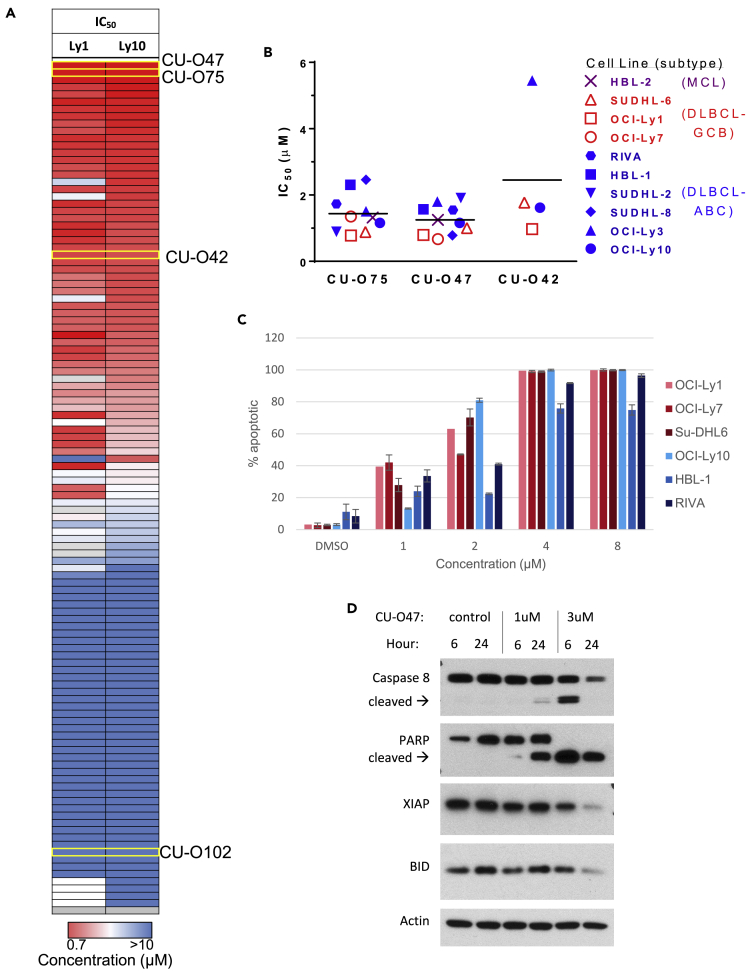
(A) Heatmap representing the activity of NQBS in inducing cell growth inhibition in 2 DLBCL lines (OCI-Ly1 and OCI-Ly10), measured by IC50 values using an ATP-based luminescence viability assay at 72 h. Representative compounds (CU-O42, CU-O47, CU-O75, and CU-O102) are highlighted. All of the experiments were performed in triplicates and repeated at least twice.
(B) NQBSs induce growth inhibition in lymphoma cell lines as measured by IC50 in an ATP-based luminescence viability assay at 24 h. Cell lines are color labeled as GCB DLBCL (red), ABC DLBCL (blue), and MCL (purple). All of the experiments were performed in triplicates and repeated at least twice.
(C) NQBSs induce apoptosis in lymphoma cell lines. PI and Yo-Pro flow cytometric analysis of CU-O42 effect in DLBCL cell lines at 24h. Cell lines are color labeled as GCB DLBCL (red) and ABC DLBCL (blue). Values represent means expressed as percentages compared with the untreated control; error bars represent SD. All of the experiments were performed in triplicates and repeated at least twice.
(D) Immunoblot analysis in OCI-Ly10 cell line treated with CU-O47 shows a cleavage of Caspase 8 and PARP, as well as a decrease in the level of XIAP and BID as markers of apoptosis induction.