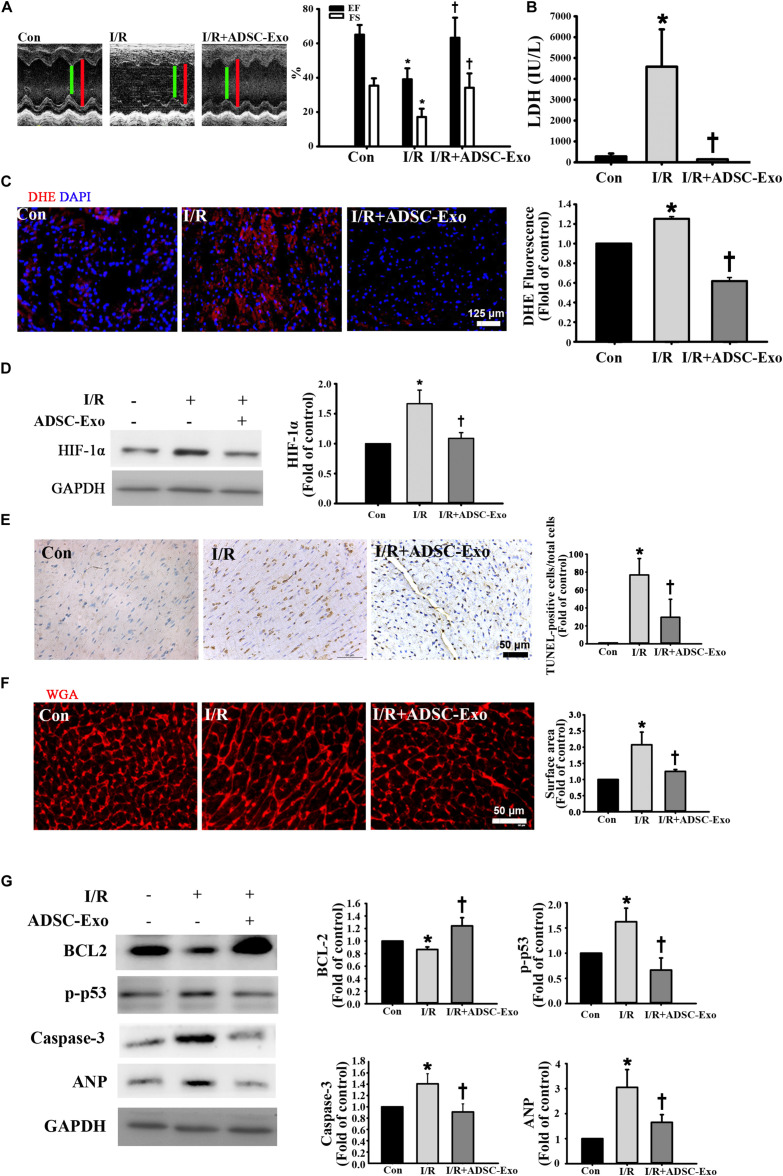
FIGURE 1.
ADSC-Exo treatment attenuated I/R-induced myocardial apoptosis and hypertrophy in vivo. Mice were subjected to ischemia for 30 min followed by reperfusion for 3 h. In the I/R + ADSC-Exo mouse model, 25 min after occlusion, ADSC-Exo (100 μg protein in 50 μL) were injected uniformly intramuscularly into five positions in the border zone of the left ventricular anterior wall and then perfused for 3 h. (A) Representative M-mode images from control mice, I/R-treated mice, and ADSC-Exo-treated I/R mice. The left ventricular ejection fraction (EF) and fractional shortening (FS) in the ADSC-Exo-treated I/R mice were significantly increased compared with those in I/R-treated mice. (B) The level of lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) release. (C) Measurement of intracellular ROS by DHE staining. Scale bar, 125 μm. A quantitative analysis of DHE fluorescence is shown. (D) Western blot analysis of the level of HIF-1α expression. (E) Effect of ADSC-Exo on apoptosis after myocardial I/R injury by TUNEL assay. (F) Quantitative analysis of cardiomyocyte cross-sectional area by WGA staining is shown. Heart sections were stained with WGA staining, and the cardiomyocyte cross-sectional area was determined. Cell image analysis of the relative cell surface area (cell size) was performed. Scale bar, 50 μm. (G) The levels of BCL2, p-p53, caspase-3, and ANP protein were evaluated by Western blot analysis. Data are expressed as the mean ± SD (n = 3). *P <0.05 vs. the control group; †P <0.05 vs. I/R group.