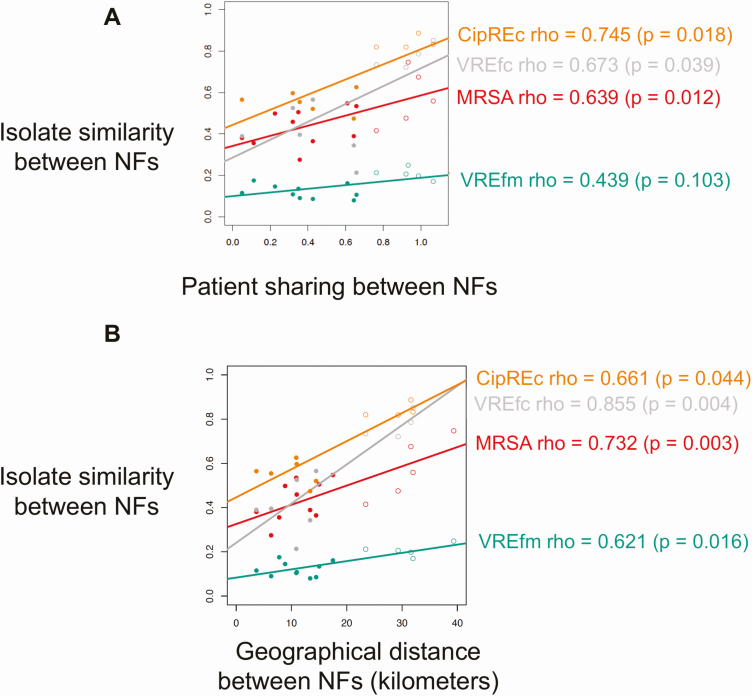
Figure 3.
Genomic relatedness among antibiotic-resistant organisms (AROs) isolates from different nursing facilities (NFs) associated with patient sharing and geographic proximity. Relationship between the genomic similarity of isolates between each pair of nursing facilities (NFs) and overlap in feeder acute care hospitals (ACHs) between the NF pair (A), and geographical distance between NF pair (B). Patient sharing between NFs (x-axis, A) indicates the extent of divergence in the proportion of patients from feeder ACHs between 2 NFs. Lower values indicate higher similarity. Isolate similarity (y-axis, A and B) indicates the divergence of the population structure of each ARO. Lower values indicate more genomic homogeneity between 2 NFs. Spearman rank correlation coefficients are shown on the right. The colors of the data points and regression lines correspond to different AROs. Closed circles denote NF pairs excluding facility 1; open circles denote NF pairs including facility 1. Abbreviations: CipREc, ciprofloxacin-resistant Escherichia coli; MRSA, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus; NF, nursing facility; VREfc, vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecalis; VREfm, vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecium.