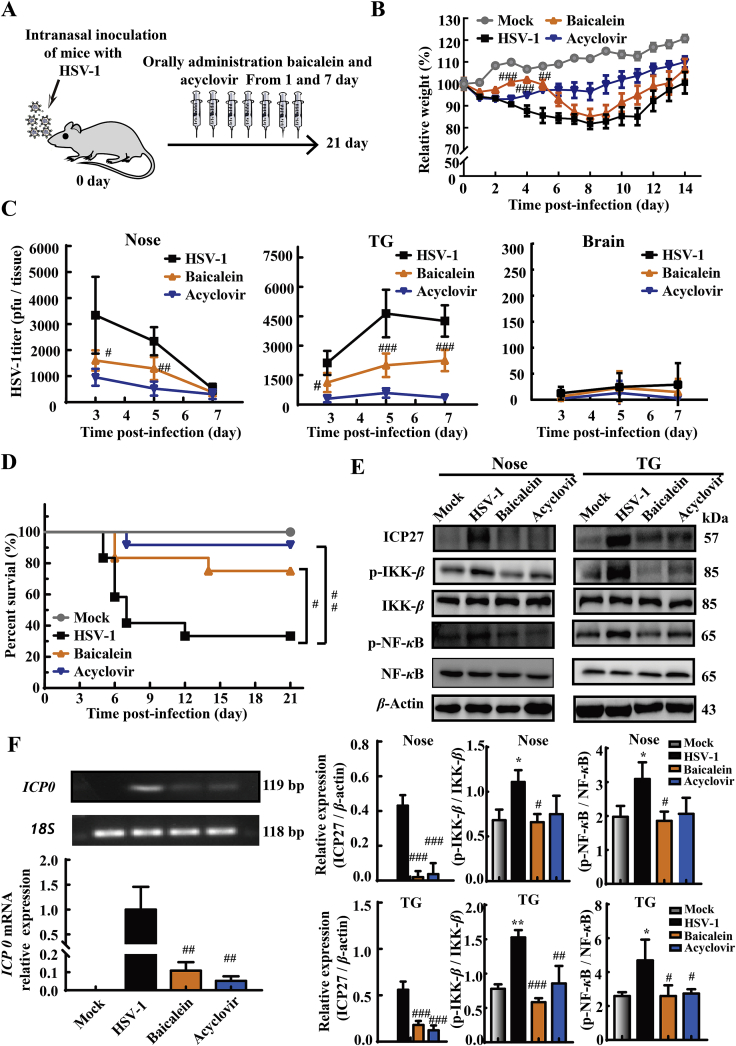
Figure 7.
Baicalein reduced HSV-1-induced lethality and tissue viral loads of mice. Mice were intranasally challenged with HSV-1/F strain (1 × 106 PFU), and then treated with baicalein (200 mg/kg/day) or acyclovir (50 mg/kg/day) for 7 consecutive days. Saline (0.9%) was used in Mock and HSV-1 groups. (A) The schema picture illustrated the protocol of baicalein and acyclovir treatment. (B) The relative body weight of mice was monitored for 14 consecutive days after infection (n = 12). (C) The infectious virions in the nose, TG, and whole brain of mice were measured by PFU assay at the 3, 5, and 7 dpi (n = 5). (D) The survival rates of mice were monitored for 21 consecutive days (n = 12). (E) Protein expressions of ICP27, p-IKK-β, IKK-β, p-NF-κB, NF-κB and β-actin in nose and TG tissues were determined at 5 dpi by Western blot assay (n = 3). (F) The expression level of ICP0 mRNA in TG tissues was analyzed by RT-qPCR at 5 dpi (n = 4–5). Data are shown as mean ± SD. ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01 vs. Mock group; #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01, ###P < 0.001 vs. HSV-1 group.