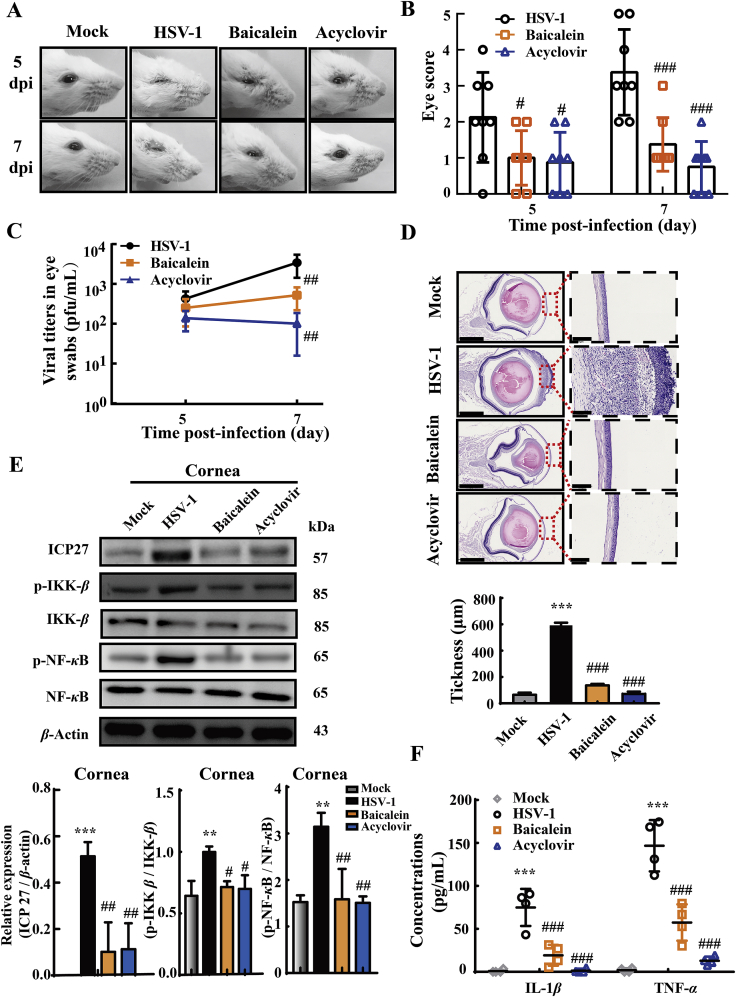
Figure 8.
Baicalein ameliorated HSV-1-associated corneal disease pathologies. Mice were corneally inoculated with HSV-1/F and orally administrated with baicalein (200 mg/kg/day) or acyclovir (50 mg/kg/day) for 7 consecutive days. (A) Representative photographs were taken from the right eyes of mice. (B) Ocular disease scores were calculated according the criteria: 0, no symptoms; 1, mild swelling of the eyelids; 2, moderate swelling of the eyelids with some crusting; 3, moderate swelling of the eyelids with >50% crusting; 4, severe crusting; 5, eye completely swollen shut (n = 8). (C) The secreted virus titers were measured from the right eyes of mice at 5 and 7 dpi (n = 5). (D) Representative corneal histology sections were taken from the right eyes of mice at 9 dpi and corneal thickness were assessed by histology (n = 4). Scale bars = 1 mm. (E) The protein expressions of ICP27, p-IKK-β, IKK-β, p-NF-κB, NF-κB and β-actin in mouse corneal tissues were determined by Western blot assay at 9 dpi (n = 3). (F) The levels of IL-1β and TNF-α in eye tissue lysate were measured by ELISA at 9 dpi (n = 4). Data are shown as mean ± SD. ∗∗P < 0.01, ∗∗∗P < 0.001 vs. Mock group; #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01, ###P < 0.001 vs. HSV-1 group.