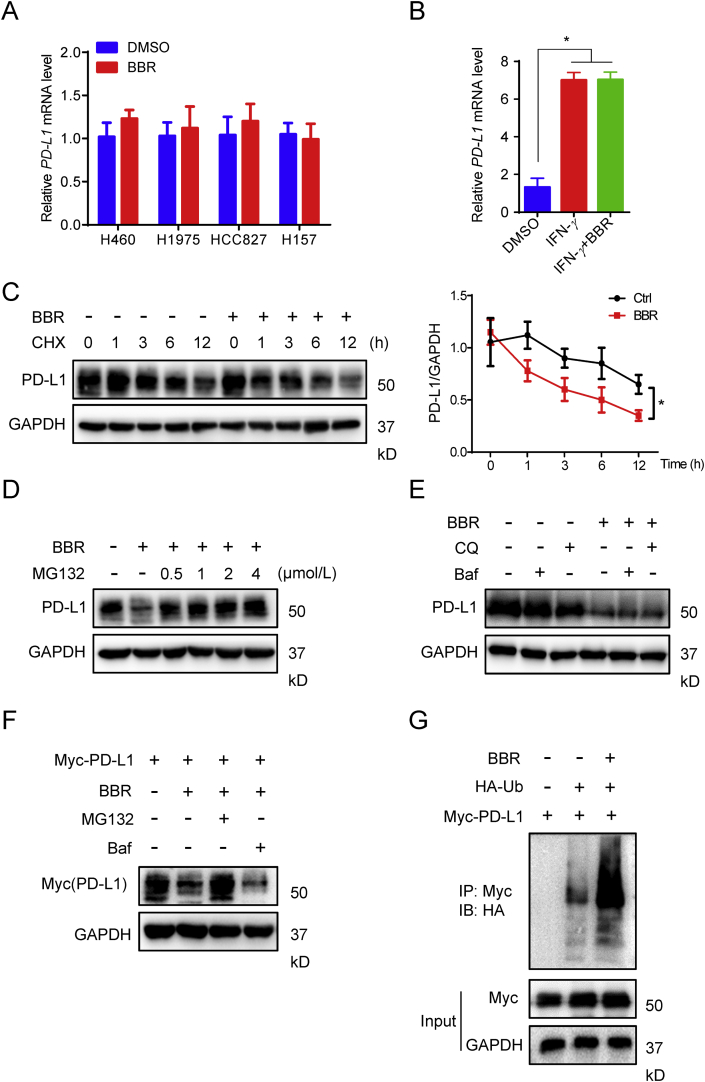
Figure 5.
BBR induces ubiquitin-dependent PD-L1 degradation. (A) and (B) Quantitative RT-PCR analysis of the mRNA level of PD-L1 in H460, H1975, HCC827 and H157 cells treated with BBR (10 μmol/L, 12 h) (A) or in A549 cells treated with BBR (10 μmol/L) and 5 ng/mL IFN-γ for 12 h (B). ∗P < 0.05 compared with DMSO group. (C) IB analysis of the PD-L1 expression in H460 cells treated with DMSO or BBR (10 μmol/L) for the indicated time points in the presence of CHX (25 μg/mL). Quantification of PD-L1 intensity is shown in right (n = 3). The abundance was normalized to GAPDH; each group was normalized as a percentage of that at 0 h. ∗P < 0.05 compared with DMSO group. (D) and (E) IB measuring the PD-L1 expression in H460 cells pre-treated with indicated concentration of MG132 (D), 200 nmol/L Baf or 100 μmol/L CQ (E), followed by 10 μmol/L BBR treatment for 24 h in the presence of CHX (25 μg/mL). (F) H1975 cells were transiently transfected with Myc-PD-L1 for 24 h, followed by Baf or CQ pretreatment for 1 h and BBR treatment for 24 h, PD-L1 level was analyzed by Myc antibody. (G) HEK293T-cells were transiently transfected with the indicated constructs. Ubiquitinated PD-L1 was immunoprecipitated (IP) and subjected to IB analysis with the ubiquitin antibody. Cells were treated with MG132 prior to ubiquitination analysis. Data shown are mean value of three independent experiments±standard error of mean (SEM). ∗P < 0.05 compared with DMSO group.