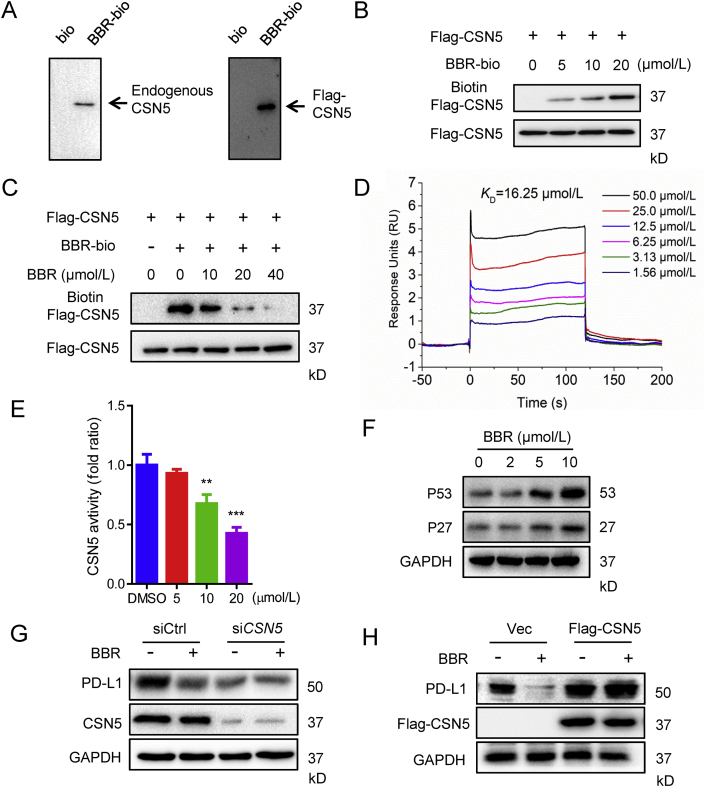
Figure 6.
BBR directly binds to and inhibits CSN5 activity. (A) The 293T or 293T expressing Flag-CSN5 cell lysates were incubated with BBR-biotin at 4 °C overnight, the lysates were used for streptavidin–agarose pull-down assays, and the precipitates were resolved by IB for CSN5. (B) The recombinant Flag–CSN5 proteins were incubated with BBR–biotin for 1 h at 37 °C, followed by IB with biotin (upper band) or Flag (lower band). (C) The recombinant Flag–CSN5 protein was incubated with BBR–biotin in the absence or presence of indicated concentration of unlabelled BBR for 1.5 h at 37 °C, and the mixtures were IB for biotin or flag. (D) SPR analysis of the binding between BBR and CSN5. Recombinant human CSN5 protein was immobilized on an activated CM5 sensor chip, BBR was then flowed across the chip. (E) CSN5 activity in an in vitro deubiquitination assay. The activity was measured by 7-amino-4-methylcoumarin (AMC) released from the fluorogenic substrate, ubiquitin–AMC (n = 3). ∗∗P < 0.01 and ∗∗∗P < 0.001 compared with DMSO group. (F) IB analysis of the P53 and P27 levels in H460 cells treated with indicated concentration of BBR for 24 h. (G and H) H460 cells were transfected with siRNA control, siRNA targeting CSN5 for 24 h (G), or transfected with 2 μg empty vector, 2 μg Flag–CSN5 for 24 h (H), followed by BBR (10 μmol/L) treatment for 24 h, the PD-L1 expression level was determined by IB. Data shown are mean value of three independent experiments±standard error of mean (SEM).