Table 2. Complex-Formation Constants, Kabs and Kem, between Ce3+ and Carboxylic Acids Other Than DGA in Aqueous Solutions Obtained from Their Absorption and Emission Spectra, Respectively, with the Relative Uncertainty of Kabs with Respect to Kema.
| ligand | pH | Kabs/M–1 | Kem/M–1 | 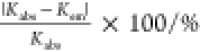 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CH3COOH | 4.73 (4.56)b | 42.0 | 40.7 | 3.10 |
| CH3CH2COOH | 4.87 (4.67)b | 44.6 | 44.9 | 0.67 |
| ClCH2COOH | 2.87 (2.68)b | 8.32 | 8.63 | 3.73 |
| CF3COOH | 0.60 (0.0)b | ∼0 | ∼0 | |
| CH3OCH2COOH | 3.53 (3.57)b | 36.8 | 40.2 | 9.24 |
| CH2(CH2COOH)2c : GLA | 3.50 | 21.9 | 23.4 | 6.85 |
| 4.00 | 48.2 | 46.1 | 4.36 | |
| 4.50 | 116 | 119 | 2.59 |
Ionic strength I = 0.1 M at room temperature (∼20 °C).
Note that each solution involving a monocarboxylic acid was set to a particular pH to attain equal rates of protonation and deprotonation, such that each value of the adjusted pH became equivalent to that of pKa at 20 °C in parentheses.54
Acid dissociation constants of GLA: pKa1GLA = 4.34, pKa2 = 5.41 at 20 °C.54
