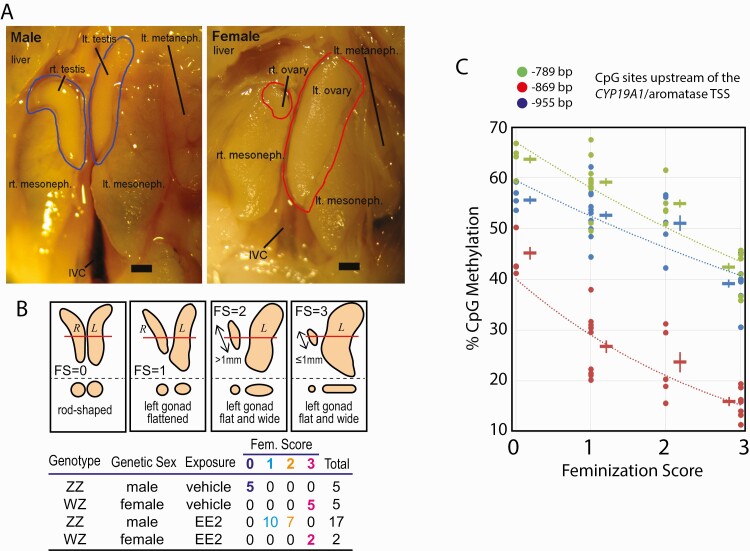
Figure 1.
Feminization of chicken embryonic gonads by exposure to 17α-ethynylestradiol (EE2). A: Morphological characteristics of normal chicken embryonic gonads at day-19 of incubation. Testes in males and ovaries in females are shown in blue and red contours, respectively. Scale bar = 1 mm. B: Feminization scores (FS) of embryonic gonads. Schematic drawings show day-19 embryonic gonads of wild type males (FS = 0), wild type females (FS = 3), and EE2-feminized genetic males (FS = 1 or 2). The bottom part of each panel shows cross sections at the level indicated by red line in the top part. Table shows 4 experimental groups with numbers and FSs of embryonic gonads involved in the present study. EE2-exposed ZW-ovaries (n = 2) were morphologically indistinguishable from nonexposed ovaries and so assigned to FS = 3. C: Demethylation of 3 sex-sensitive CpG sites in promoter of the CYP19A1/aromatase gene upon EE2-feminization of ZZ-males. Each datum point indicates bisulfite pyrosequencing determination of CpG methylation of individual gonad. Cross symbols indicate mean ± SEM of DNA methylation at each CpG site and experimental group. Abbreviations: CpG, 5’-C-phosphate-G-3’; DNA, deoxyribonucleic acid; IVC, inferior vena cava; SEM, standard error of mean.