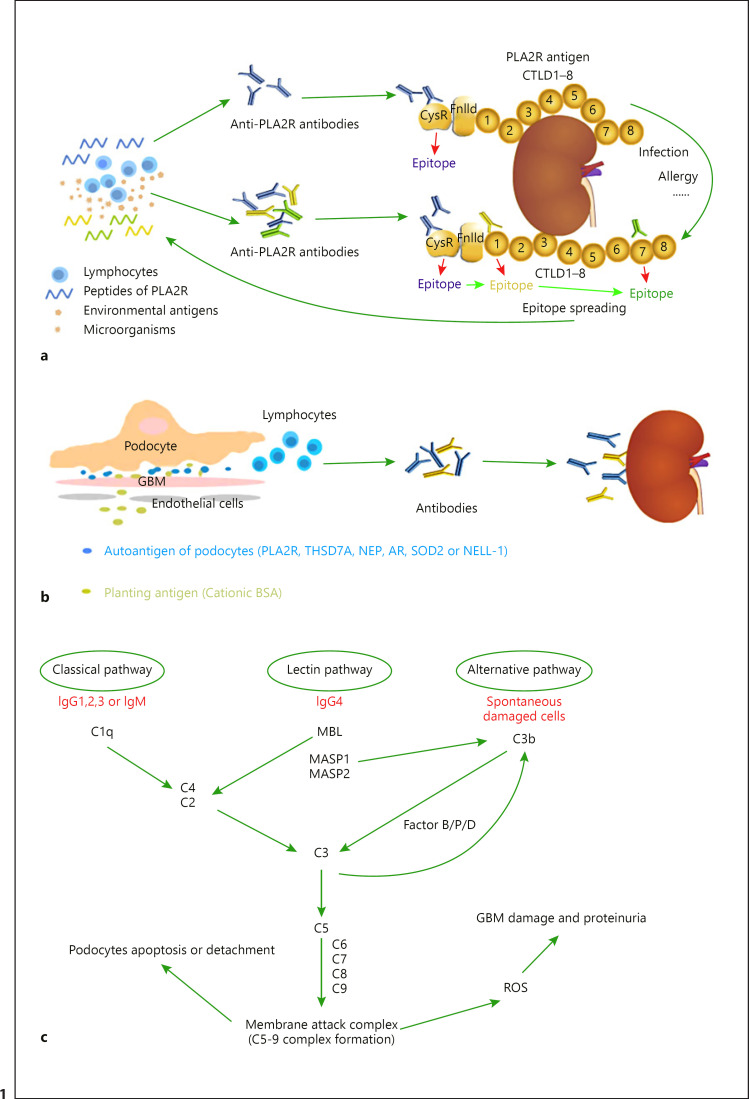
Fig. 1.
Mechanisms of kidney injury in MN. a The peptides of PLA2R released by podocytes or other cells, and molecular simulation of PLA2R epitopes by microorganisms or other environmental antigens, triggering immune response, enable lymphocytes to produce anti-PLA2R antibodies to attack PLA2R in the kidney. The extracellular segment of the phospholipase A2 receptor (PLA2R) contains an N-terminal CysR region, an FnIID, and a tandem repeat of eight CTLDs. The major antigen epitope of PLA2R is in CysR which can be bound by anti-PLA2R antibodies. A second immune challenge (allergy, infection, etc.) induces epitope spreading from CysR toward CTLD1 and CTLD7, which induces more anti-PLA2R antibodies and exacerbates renal injury. bThe immune system recognizes the endogenous integral membrane proteins of the podocyte or exogenous antigens planted in the glomerulus and produces antibodies that attack the kidney. c Complement can be activated by three different pathways in IMN. The C5b-9 membrane attack complex is formed after the activation of complement, which induces the production of ROS, leading to GBM damage and proteinuria, and causes apoptosis and exfoliation of podocytes directly, leading to a reduced number of glomerular podocytes. PLA2R, phospholipase A2 receptor; THSD7A, thrombospondin type-1 domain-containing 7A; CysR, cysteine-rich ricin domain; FnIID, fibronectin-like type II domain; CTLD, C-type lectin-like domain; NEP, neutral endopeptidase; BSA, bovine serum albumin; ROS, reactive oxygen species; GBM, glomerular basement membrane; SOD2, superoxide dismutase 2; AR, aldose reductase; NELL-1, neural epidermal growth factor-like 1 protein; GBM, glomerular basement membrane; Ig, immunoglobulin; MBL, mannose-binding lectin; MASP, mannan-binding lectin-associated serine protease; MN, membranous nephropathy.