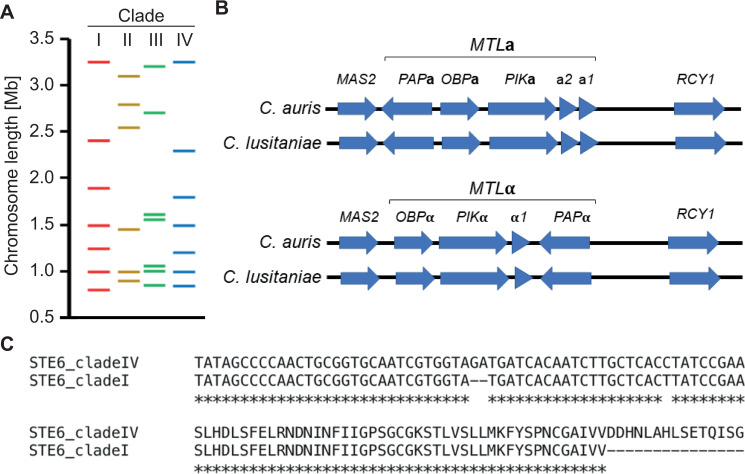
Fig 1. Chromosomal and genetic features of C. auris related to sexual reproduction.
(A) Length and number of chromosomes of 1 isolate from each of the 4 main C. auris clades as measured by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (strains representing clades are: clade I, UACa1/470026; clade II, UACa18/B11220; clade III, UACa20/B11221; clade IV, UACa22/B11244) [14]. (B) The mating type locus regions MTLa and MTLα are conserved between C. auris and C. lusitaniae [26]. (C) ClustalΩ (https://www.ebi.ac.uk/Tools/msa/clustalo/) [38] alignments of the STE6 nucleotide sequences (top) from a clade I and a clade IV isolate, showing the 2-nucleotide deletion in clade I; and of the translated sequences (bottom) showing the premature stop codon in the clade I isolate at position 421 generated by the 2-nt deletion [36].