Figure 6.
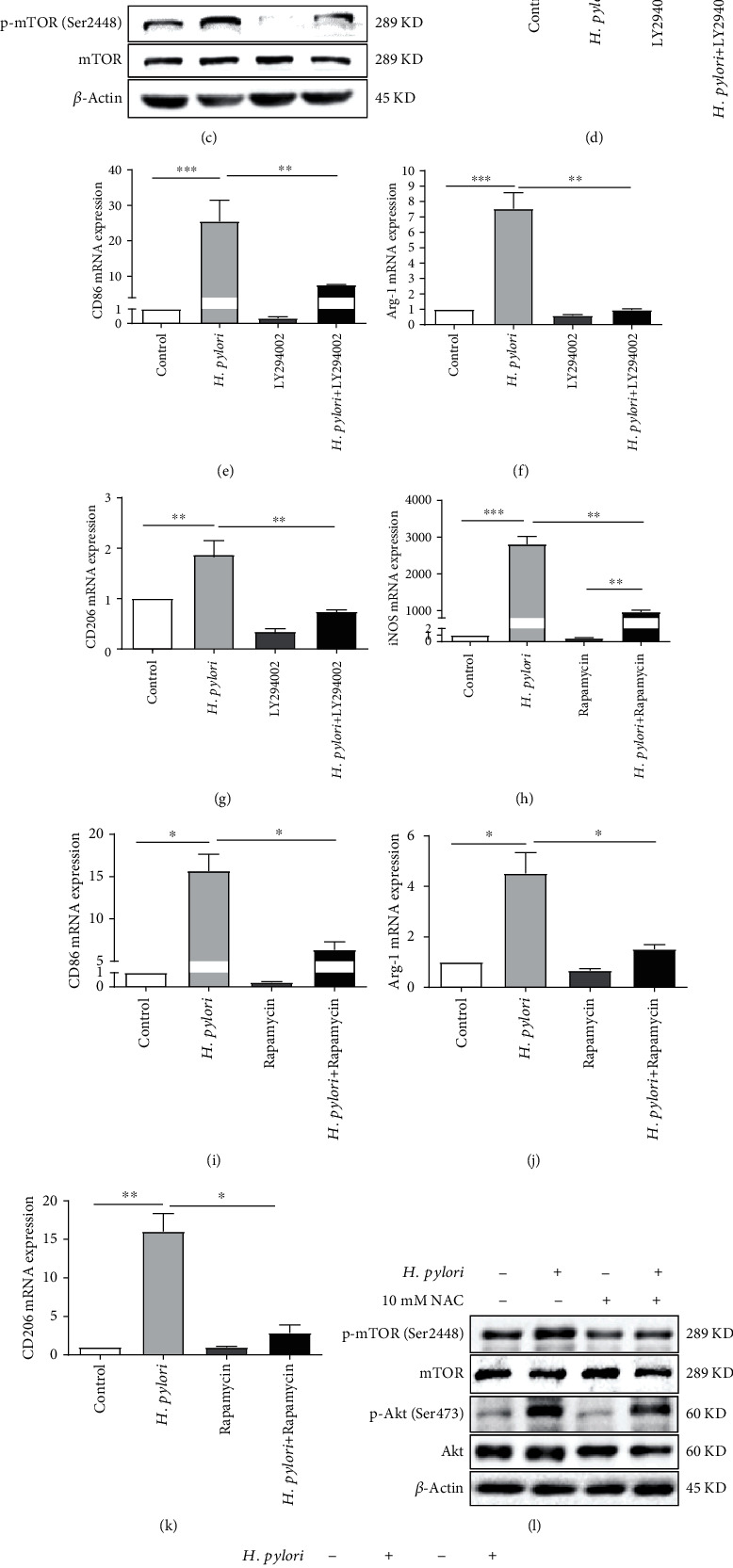
ROS and HIF-1α regulated H. pylori-induced macrophage polarization via the Akt/mTOR pathway. Increased expression of p-mTOR (Ser2448) and p-Akt (Ser473) was observed in RAW 264.7 cells treated with H. pylori at different MOIs for 9 h (a). RAW 264.7 cells were treated with H. pylori (MOI = 100), LY294002 (20 μmol/L), rapamycin (20 nmol/L), the combination of H. pylori and LY294002 (20 μmol/L), or the combination of H. pylori and rapamycin (20 nmol/L). LY294002 and rapamycin significantly attenuated the levels of p-Akt (Ser473) (b) and p-mTOR (Ser2448) (c), as well as the M1 (d–g) and M2 (h–k) phenotypes induced by H. pylori. RAW 264.7 cells were incubated with H. pylori (MOI = 100) alone or in combination with NAC (10 mM) (l) or YC-1 (10 μM) (m). Both NAC and YC-1 treatment reduced the augmented p-mTOR (Ser2448) and p-Akt (Ser473) levels induced by H. pylori. All experiments were independently repeated three times.
