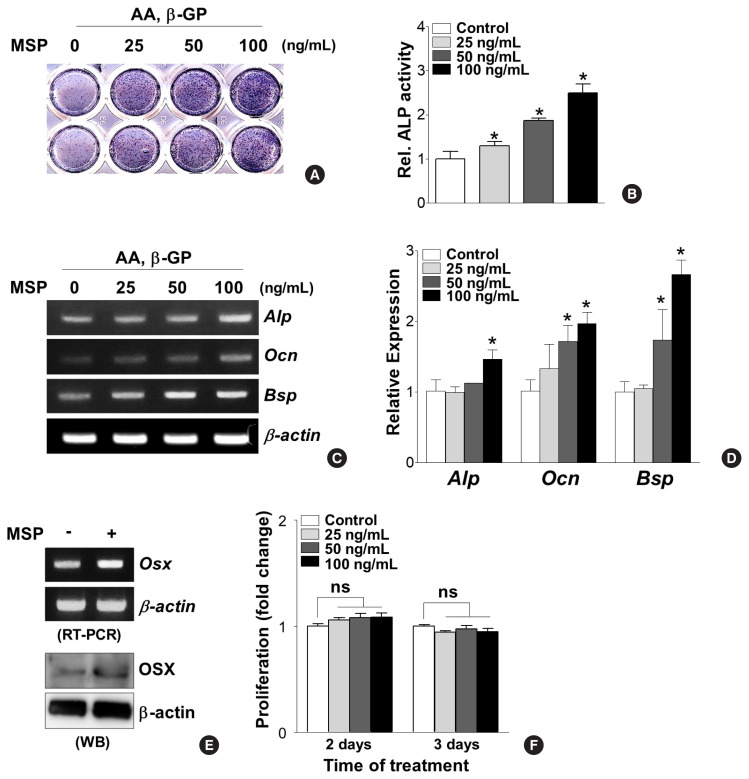
Fig. 2.
Macrophage-stimulating protein (MSP) treatment stimulates osteoblastic differentiation in primary pre-osteoblasts. (A, B) Effect of MSP treatment on alkaline phosphatase (Alp) activity. Primary pre-osteoblasts were cultured with MSP (25–100 ng/mL) in osteogenic medium, containing ascorbic acid (AA) (50 μg/mL) and β-glycerophosphate (β-GP) (5 mM) for 9 days. The cells were subjected to analyzing ALP staining analysis (A) and quantitative ALP activity (B). *P<0.05 vs. control. (C, D) Effect of MSP treatment on expression of osteoblast specific genes. Cells were cultured with MSP (25–100 ng/mL) for 6 days. Total RNA was isolated, and reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) or quantitative RT-PCR (qRT-PCR) was performed with ALP, osteocalcin (Ocn), bone sialoprotein (Bsp) primers. Their relative expression is calculated after normalization to the levels of β-actin. *P<0.05 vs. control. (E) Effect of MSP treatment on the expression of osterix (Osx). Cells were cultured with MSP (100 ng/mL) for 3 days. RT-PCR (upper panel) and Western blotting analyses (lower panel) were performed. (F) Effect of MSP on proliferation of primary pre-osteoblasts. The cells were cultured with MSP (25–100 ng/mL) for 2 and 3 days, and cell proliferation was evaluated using WST-1 assay reagents. ns, not significant.