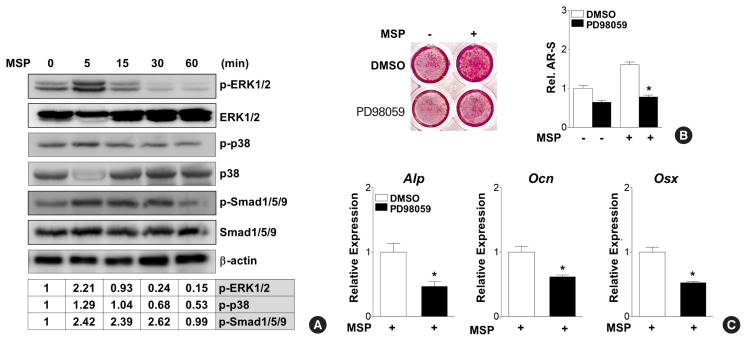
Fig. 5.
Extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) signaling pathway mediates macrophage-stimulating protein (MSP)-induced osteoblast differentiation. (A) Western blot analysis using the indicated antibodies shows effects of MSP on several signaling molecules. C3H10T1/2 cells were treated with MSP (100 ng/mL) in non-osteogenic medium for the indicated time. Relative levels of phosphorylation of ERK1/2, p38, and Smad1/5/9 are expressed as the ratio of phosphorylated forms to total protein levels normalized to untreated control. (B) Effects of the ERK inhibitor, PD98059, on MSP induction of calcium deposition. Cells were pre-treated with the PD98059 (10 μM) in osteogenic medium, and then MSP (100 ng/mL) was added. After 21 days, the cells were stained with alizarin red solution (left panel). To quantify calcium deposition, the stained samples were reacted with 10% cetylpyridinium chloride, and the absorbance of elution solution was measured by spectrophotometry (right panel). Each bar shows 3 independent experiments. *P<0.05 vs. control. (C) Effects of an ERK specific inhibitor on MSP-treated gene expression. Cells were pre-treated with the ERK1/2 specific inhibitor PD98059 (10 μM) in osteogenic medium, and then MSP (100 ng/mL) was added. After 7 days, cells were harvested and quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) was performed. Alp, alkaline phosphatase; Ocn, osteocalcin; Osx, osterix.