Figure 6:
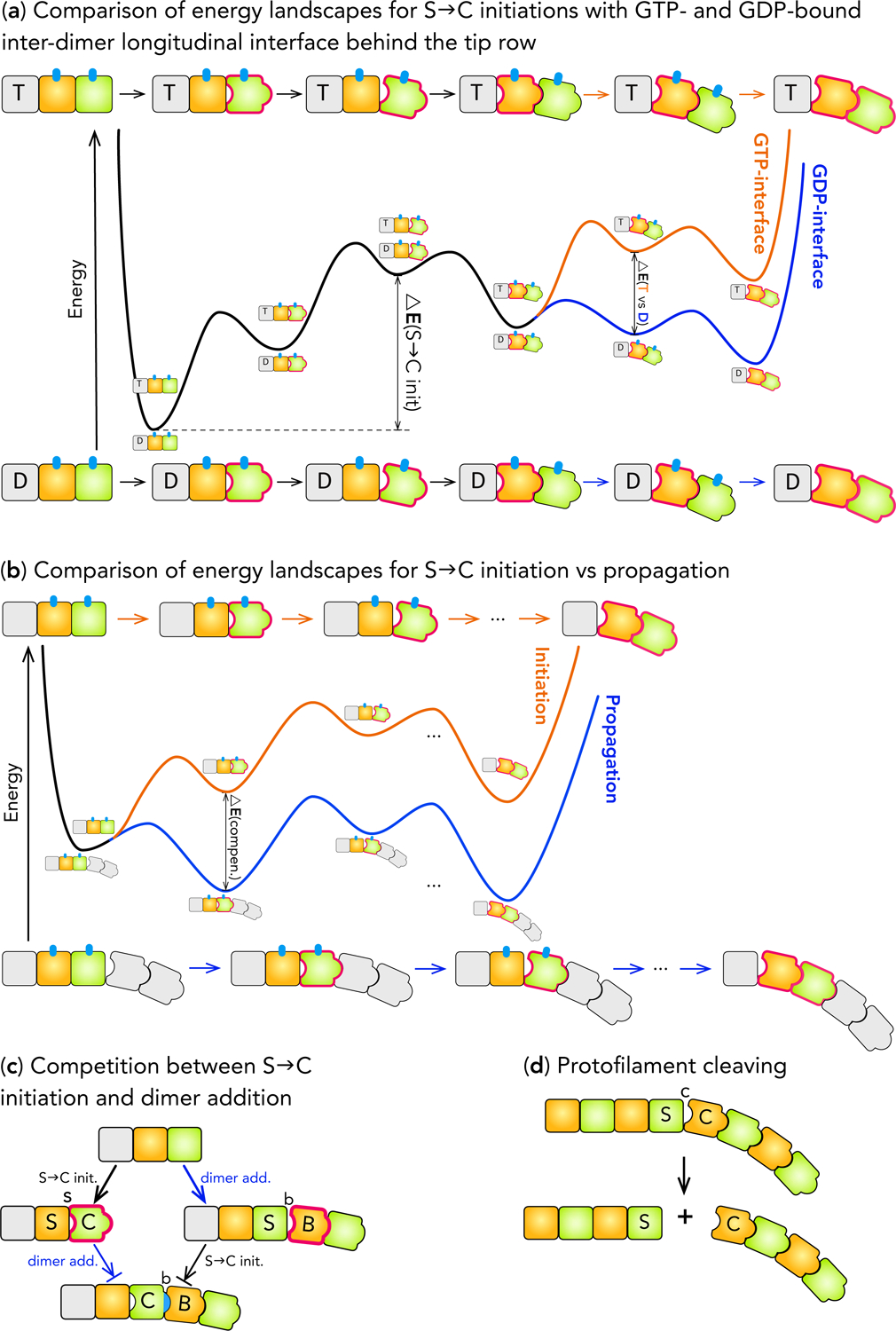
ELs for S→C initiation and propagation at the plus-end. (a) The energy landscapes for S→C initiation at plus-end with GTP- (Orange) and GDP-bound (Blue) inter-dimer longitudinal interface behind the tip row. The major energy barrier for GDP-bound interface, ΔE (S→C init.), and the extra energy required at GTP-bound interface,, are marked. (b) Comparison of the energy landscapes for S→C initiation (Orange) ΔE (T vs. D) and propagation (Blue). The decrease in the energy barrier for propagation due to the energy compensation effect, (ΔE compen.), is marked. (c) Schematic showing that S→C initiation and dimer addition compete with each other and are mutually exclusive. A block-end arrow (⇥) indicates that a reaction is inhibited and unlikely to occur. (d) Schematic showing PF cleaving during shortening.
