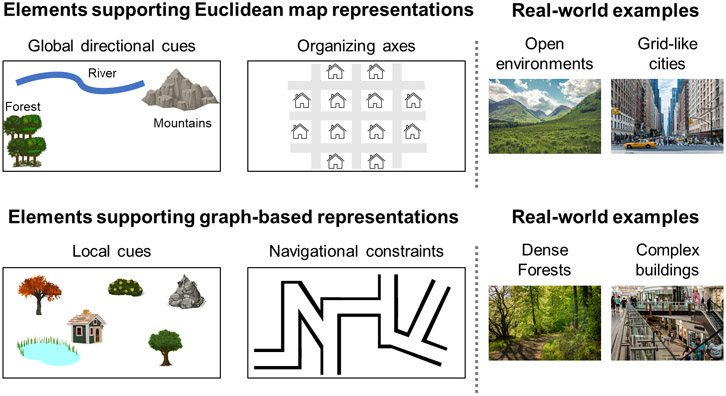
Figure 4: Environmental features supporting map-based and graph-based representations.
Euclidean representations are supported when the environment contains global directional cues (e.g. distal landmarks, slopes) or prominent defining axes. These representations may be favored in open environments, small co-visible spaces like single rooms, and in cities with a grid-like structure. In contrast, graph-based representations are supported by the presence of local landmarks and may be optimal when navigation is constrained to specific routes. Therefore, graph-based representations might be favored in dense forests, complex buildings, and cities without clear organizing axes.