Extended Data Figure 2: Conformational changes in MEK and KSR upon binding to trametinib.
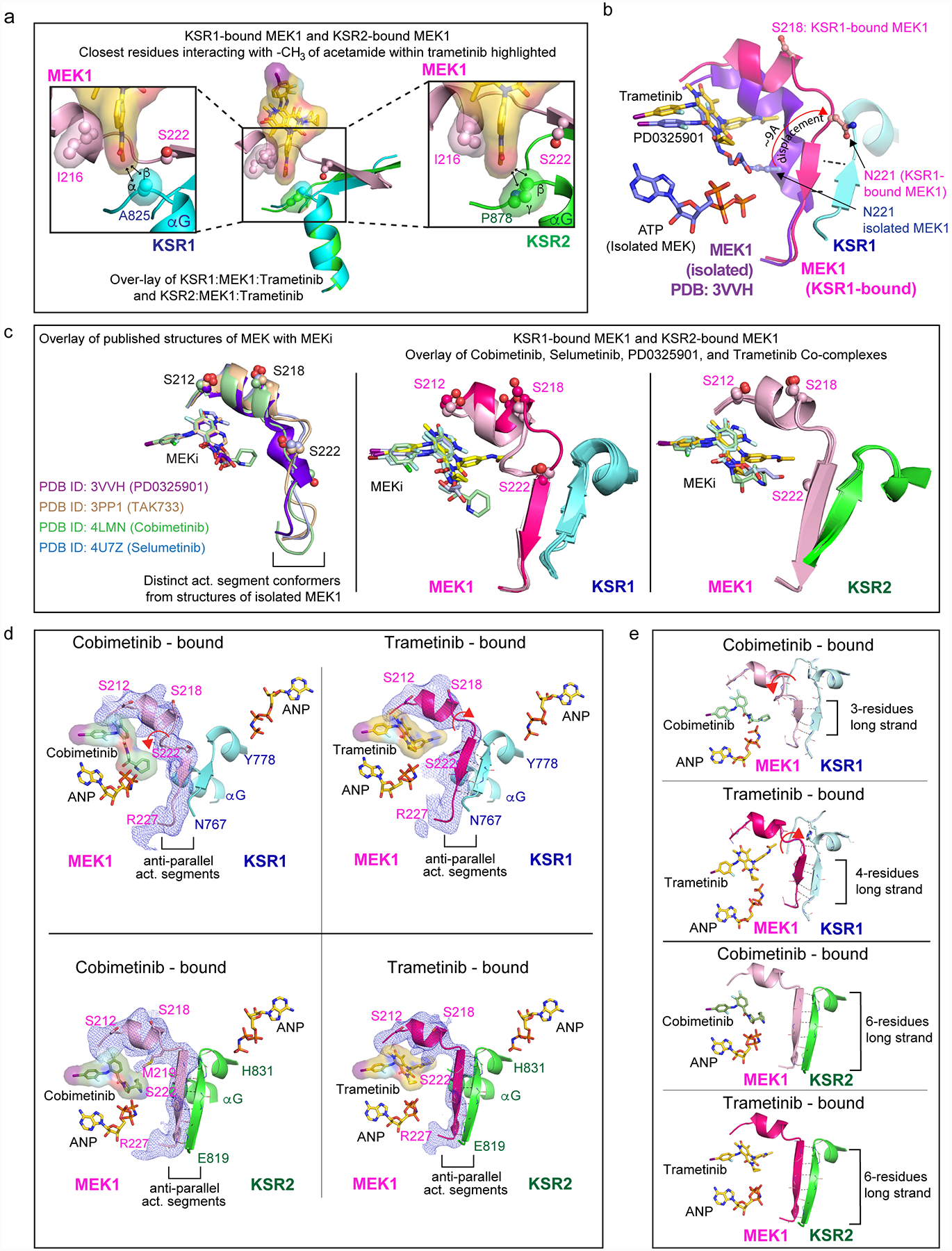
A. Close-up view of the trametinib interactions with KSR1 (left) and KSR2 (right). The terminal acetamide group of trametinib stacks between I216 in MEK1 and A825 in KSR1 or P878 in KSR2. Distances with hydrogens included in the models of trametinib and KSR measure 2.4 Å and 3.5 Å between alpha and beta hydrogens of A825 in KSR1 and the terminal -CH3 of trametinib. In comparison, the terminal -CH3 of trametinib measures 2.2 Å and 3.1 Å from beta and gamma hydrogens of P878. Measurements are marked by black arrows. Ser222 at one end of the anti-parallel activation segments between MEK and KSR is highlighted.
B. The MEKi allosteric pocket, and activation segment displacement, between the isolated state of MEK1 bound to PD0325901 relative to the KSR1:MEK1 complex bound to trametinib. The displacement in the activation segment was measured based on movement of residue Asn221 in the isolated and KSR1-bound state of MEK1.
C. Left: distinct activation loop conformers of isolated MEK1 have been observed in complex with PD0325901 (purple; PDB ID 3VVH), TAK733 (light brown; 3PP1), selumetinib (light blue; 4U7Z), and cobimetinib (light green; 4LMN). Middle and Right: overlay of the KSR1:MEK1 and KSR2:MEK1 structures bound to the indicated MEKi reveal near identical activation segment conformers, with the exception of the trametinib-bound complex of KSR1:MEK1.
D. Comparison of activation loop conformations in cobimetinib-bound (left) and trametinib-bound (right) states of the KSR1:MEK1 (top) and KSR2:MEK1 (bottom) complexes. Fo-Fc omit electron density map, contoured at 2.0 σ, with a 3.0 Å cutoff, around the activation loop is shown as a blue mesh. Movement of the MEK activation loop between the two inhibitor-bound states of KSR1:MEK1 is highlighted by a red arrow. Main chain H-bonds between the anti-parallel beta strands in KSR and MEK are shown as dotted lines.
E. In the trametinib bound KSR1:MEK1 complex, a four-residue anti-parallel beta strand structure is formed between KSR1 and MEK1. In comparison, the same region forms a three-residue stretch in all other KSR1:MEK1 structures that we determined; the cobimetinib-bound complex is shown as an example for comparison. In contrast, a six-residue long anti-parallel beta strand is formed in the KSR2:MEK1 structures, irrespective of bound MEKi. The three- and four- residue long strands in KSR1:MEK1 include residues 769–771/772 for KSR1 and 222/223–225 for MEK1. The six residue long strands in KSR2:MEK1 include residues 820–825 for KSR2 and 221–226 for MEK1.
