Extended Data Figure 4: Intracellular target engagement on MEK and KSR-bound MEK via bioluminescence resonance energy transfer.
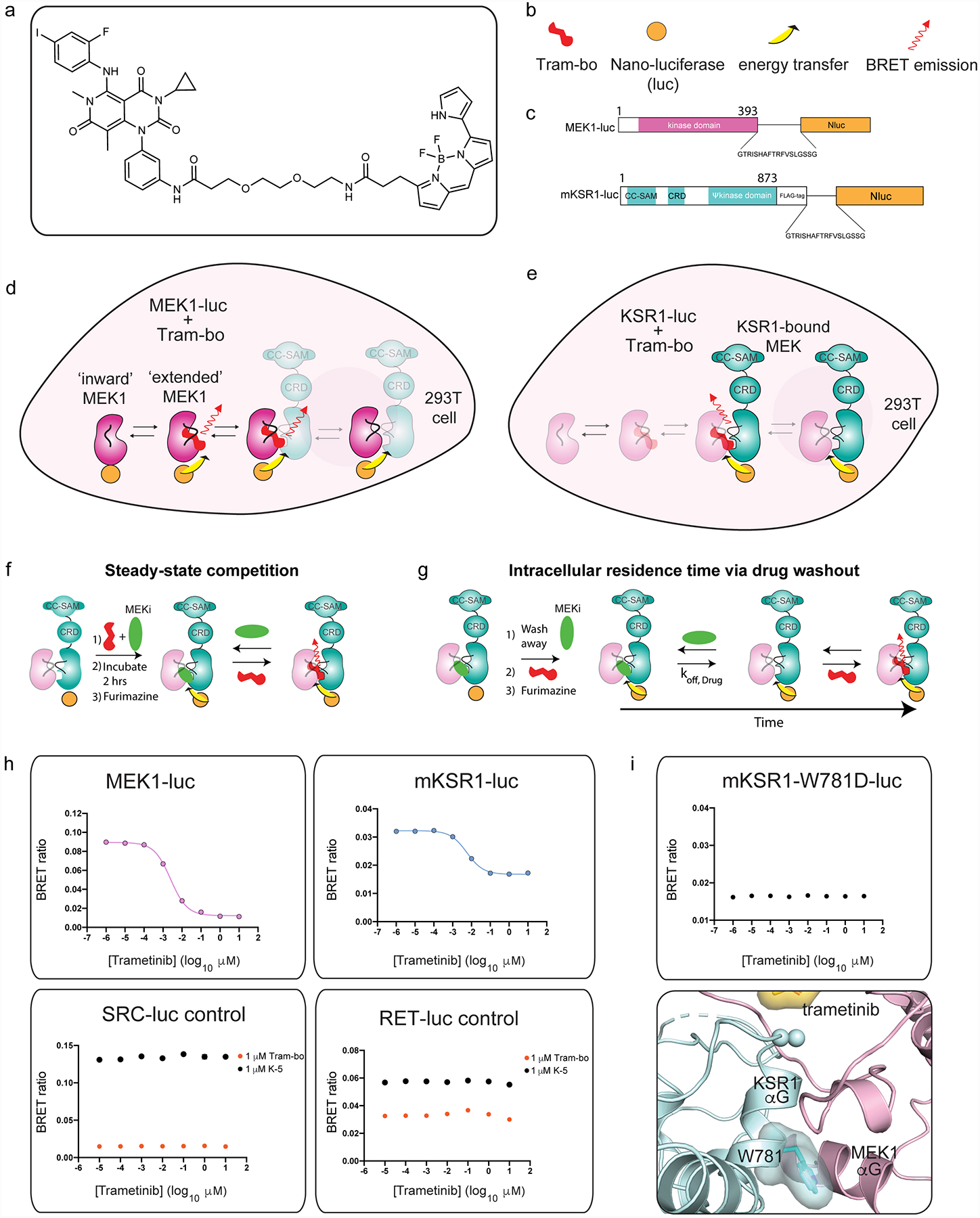
A. Chemical structure of trametinib-bodipy. We refer to this fluorescent probe compound as tram-bo’.
B. Legend for schematics used in the lower panels.
C. Nano-luciferase tagged fusions of MEK (MEK-luc) and mouse KSR1 (KSR-luc).
D. BRET emission signal (red arrow) between MEK-luc and tram-bo is expected to occur within multiple distinct states of MEK, including in the KSR-bound and free states of MEK as depicted.
E. BRET emission (red arrow) between KSR-luc and tram-bo is expected to occur exclusively in the KSR-bound state of MEK as depicted.
F. Assay design for steady-state competition experiments.
G. Assay design for intracellular residence time experiments.
H. BRET signals between 1 μM tram-bo and the indicated luciferase tagged fusion proteins expressed in 293T cells. Increasing concentrations of free trametinib were added to these cells to determine IC50 values. Dose-dependent competition for free trametinib was observed on MEK-luc and mouse KSR-luc. However, no discernible dose response for trametinib was observed on controls including RET-luc and SRC-luc using either tram-bo or previously established active site tracers K5 and K442, respectively.
I. A helix αG mutant, W781D in mouse KSR1, supports that the BRET signal between wild-type KSR1 and tram-bo depends on intact complex formation between KSR and MEK within cells. In particular, the KSR1-W781D mutant does not produce any dose dependent BRET signal (using 1 μM tram-bo) due to a predicted loss of complexation with MEK1; we previously demonstrated that the W781D mutant (W884D in KSR2 numbering) is a strong loss of function in KSR with respect to ERK pathway activation, and the analogous mutation in BRAF (F667E) prevents direct binding with purified MEK29. W781 in mouse KSR1 is equivalent to W831 in human KSR1, W884 in human KSR2, and F667 in human BRAF. Structural depiction of the mouse W781 (ie. W831 in human KSR1) residue at the interface of KSR1:MEK1 complex is shown below.
